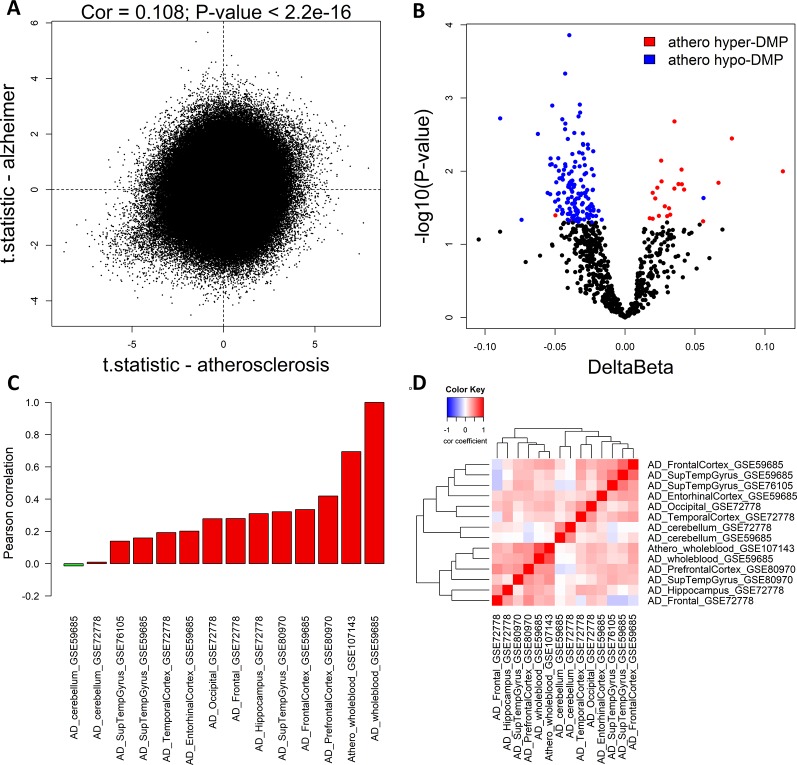
Figure 1.
Common DNA methylation signature in atherosclerosis and Alzheimer’s disease (AD) whole blood and brain samples. (A) The genome-wide significance levels (t-statistic) of each CpG-probe in the atherosclerosis (GSE107143) and AD (GSE59685) whole blood dataset was plotted in the X-axis and Y-axis, respectively. The Pearson correlation was used to calculate the correlation between the two datasets. (B) Volcano plot showing the methylation differences and statistical significance values after comparing the methylation values of the 712 top significant atherosclerosis differentially methylated positions (DMPs) (athero-DMPs) between AD patients and healthy individuals. Probes which were significantly different between AD and controls (p-value < 0.05) were colored blue when hypomethylated and red when hypermethylated in atherosclerosis. (C) Correlation coefficients between the t-statistics of the 712 athero-DMPs in the atherosclerosis whole blood dataset and the t-statistics of the athero-DMPs in multiple AD brain and whole blood datasets. Positive correlations are represented as a red bar, and negative correlations as a green bar. (D) Correlation heatmap representing the correlation coefficients between the t-statistics of the 712 athero-DMPs across different AD datasets. Red means a positive correlation and blue a negative correlation.