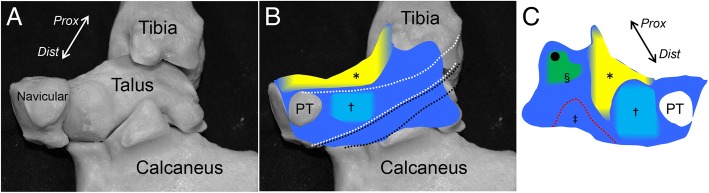
Fig. 7.
Schematic illustrations of the continuous capsule on the medial ankle. a Underlying bones of the right medial ankle on the continuous capsule. b The outer appearance of the continuous capsule is shown. The fatty tissue (yellow, asterisk) covered the anterior part of the ankle and talonavicular joints. Posterior to the insertion of the posterior tibialis tendon (PT), the cartilaginous tissue, normally referred as the SML (aqua area, dagger), located to form the gliding floor of the tendon (white dotted area). Black dotted area indicates the gliding floor of the flexor digitorum longus tendon. c The continuous capsule shown in (b) is posteriorly reflected to show the inner appearance. The fibrous tissue, normally referred as the deep deltoid ligament (green area), connects between the intercolliculus groove of medial malleolus (black circle) and the depression of the medial talus (section mark). The fatty tissue extended medially between the fibrous and the cartilaginous tissues. The cartilaginous tissue covered the talus head. Red dotted area indicates the capsular attachment on sustentaculum tali (double dagger). Prox, proximal; Dist, distal