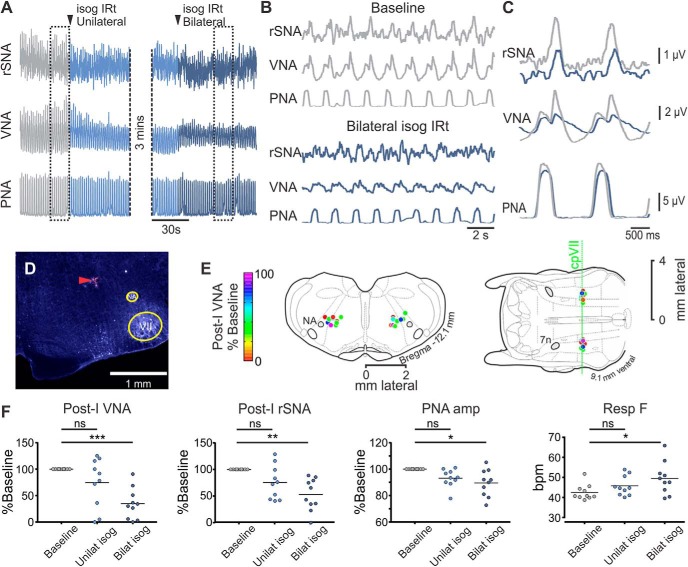
Figure 2.
IRt inhibition attenuates eupneic post-I activity. A, Experimental recording from urethane-anesthetized Lewis rat; bilateral microinjections of isoguvacine (isog) were made into the IRt. B, Expanded view of boxed regions from A and corresponding phrenic-trigged averages in C show attenuated post-I VNA and rSNA without significant effects on respiratory pattern. D, Histological section showing representative injection site marked by fluorescent beads (red arrowhead). E, Composite images represent injection sites from multiple experiments mapped onto corresponding coronal (left) and horizontal (right) atlas plates, color-coded to indicate effect of bilateral isoguvacine on post-I VNA. F, Pooled data indicate that bilateral IRt inhibition significantly reduces post-I VNA, rSNA, and PNA, and increases respiratory frequency. Dunn's post-test: ns, not significant; *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001.