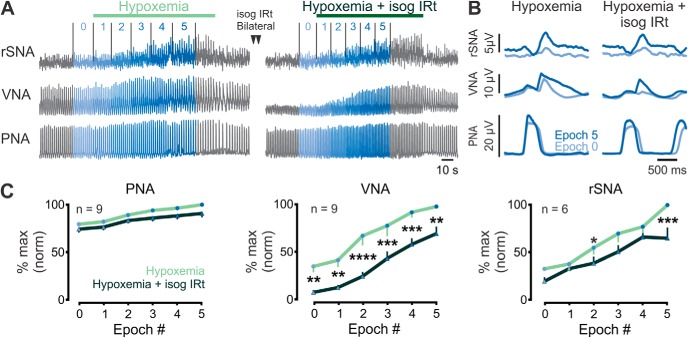
Figure 4.
Hypoxemic recruitment of post-I activity persists after IRt inhibition. A, Urethane-anesthetized rats were exposed to brief hypoxemia. Following recovery of respiratory parameters, bilateral microinjections of isoguvacine were made into the IRt and rats reexposed to hypoxemia. B, Phrenic-triggered waveform averages from the same experiment showing rSNA, VNA, and PNA responses to acute hypoxemia before (left) and after (right) bilateral IRt inhibition. C, Pooled data indicate that IRt inhibition reduces, but does not block, hypoxemic recruitment of post-I VNA or rSNA and exerts no significant effect on PNA. Significant pairings were identified using Fisher's Least Significant Difference Test: *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001.