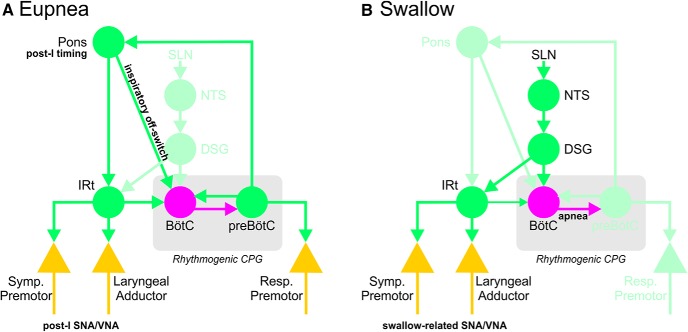
Figure 6.
Simplified schematic diagram illustrating potential integration of IRt with respiratory and swallowing network components. A, During eupnea, post-I timing originates in the pons, recruiting post-I activities in laryngeal motor and sympathetic premotor outputs via relay in the IRt. Excitatory post-I drive from the pons also activates inhibitory BötC neurons that truncate inspiration, the so-called “inspiratory off-switch.” B, Stimulation of laryngeal afferent fibers in the SLN excites second-order NTS neurons that trigger swallow via activation of the DSG. DSG activation results in powerful recruitment of BötC neurons, arresting respiratory rhythm, and activation of the ventral swallowing group located in the IRt, which transmits rhythmic swallow-related activity to respiratory and sympathetic outputs. Bright green represents excitatory components. Magenta represents inhibitory connections. Pastel green represents inactive components. Yellow triangles represent output neurons. Symp. Premotor, RVLM sympathetic premotor neurons; Resp. Premotor, respiratory premotor circuits in the rostral and caudal ventral respiratory groups.