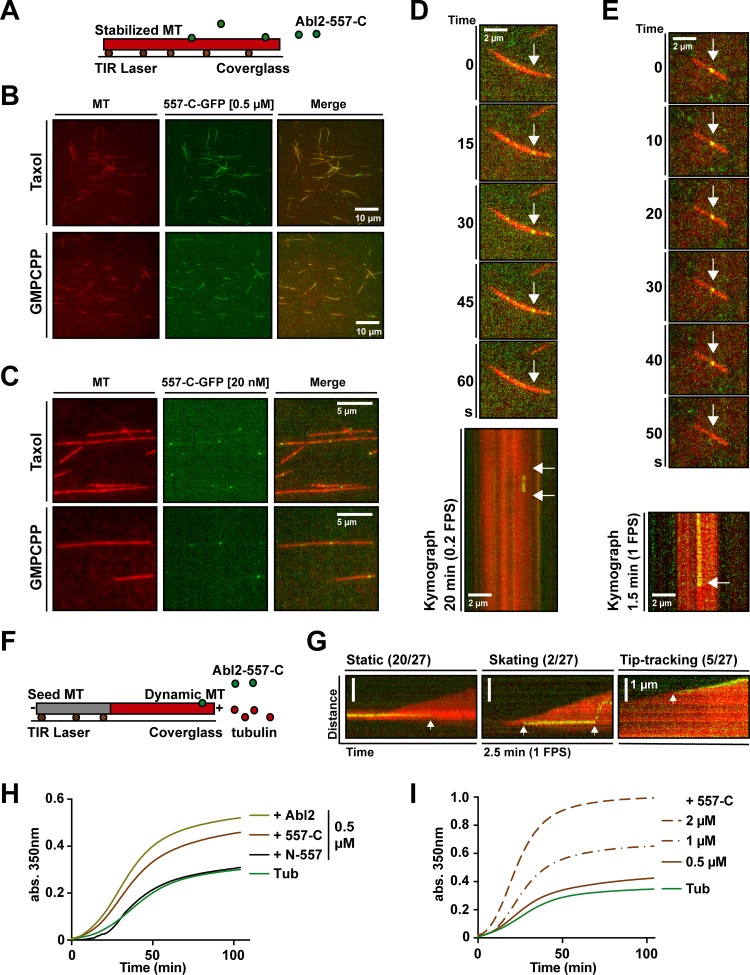
Figure 2.
Abl2-557-C-GFP binds on growing and stabilized MTs and Abl2 or Abl2-557-C promotes tubulin assembly. (A) Abl2-557-C-GFP (green) was incubated with rhodamine-labeled GMPCPP- or taxol-stabilized MTs (red) bound to the coverslip via anti-rhodamine antibodies (brown). Stabilized rhodamine-MTs were incubated with (B) 0.5 µM or (C) 20 nM Abl2-557-C-GFP. Kymographs of 20 nM Abl2-557-C-GFP on GMPCPP-stabilized MTs plotted from videos (D) at 0.2 FPS or (E) 1 FPS. (F) 50 nM Abl2-557-C-GFP and 7 µM rhodamine-tubulin was incubated with GMPCPP-stabilized biotin-MTs (gray) bound to the coverslip via neutravidin (brown). (G) Kymographs of Abl2-557-C-GFP on growing rhodamine-MTs. Events are categorized as static, skating, or tip-tracking. Tubulin assembly was monitored by measuring turbidity (A350). Representative time series of A350 measurements are shown. 18 µM tubulin and 1 mM GTP incubated alone or with (H) 0.5 µM Abl2, Abl2-557-C, or Abl2-N-557; (I) 0.5, 1, or 2 µM Abl2-557-C. n = 3. Arrows in D and E (top) show the position of single Abl2-557-C-GFP molecules binding to MTs. In the kymographs on D, E, and G, arrows mark the appearance and/or disappearance of the Abl2-557-C-GFP molecule binding and unbinding to MTs. TIR, total internal reflection.