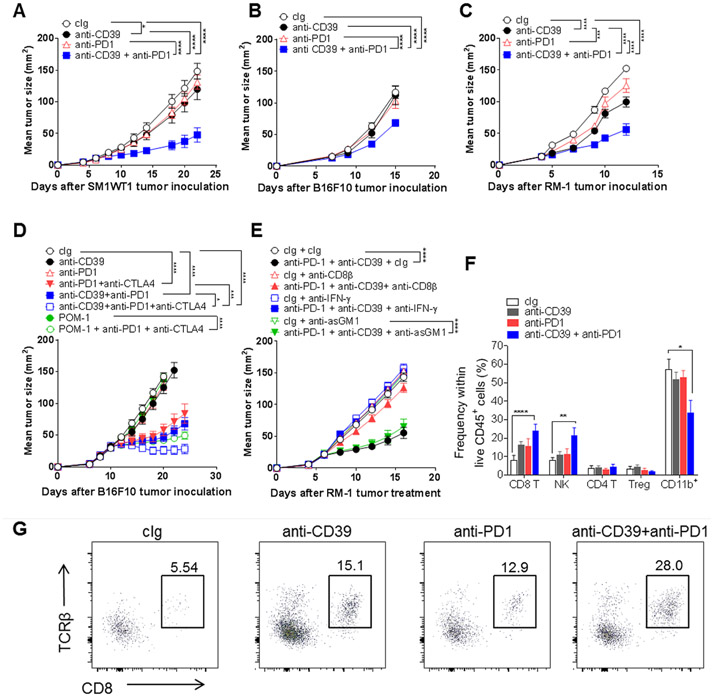
Figure 5. Anti-CD39 mAb sensitizes anti-PD1-resistant tumors by increasing CD8+ T cell infiltration.
(A) SM1WT1 tumors. Groups (n = 6/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with SM1WT1 melanoma (1 × 106) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD1 (250 μg), or anti-CD39/anti-PD1 (200 μg;250 μg) on days 6, 9, 12, and 14. (B) B16F10 tumors. Groups (n = 7-9/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with B16F10 melanoma (1 × 105) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD1 (250 μg), anti-CD39/anti-PD1 (200 μg;250 μg) on days 7, 10, and 13. (C) RM-1 tumors. Groups (n = 7-8/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with RM-1 prostate carcinoma cells (5 × 104) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD1 (250 μg), anti-CD39/anti-PD1 (200 μg;250 μg) on days 3, 6, 9, and 12. (D) Combining anti-CD39, anti-PD1 and anti-CTLA4 improves therapeutic efficacy in resistant B16F10 tumors. Groups (n = 6-12/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with B16F10 melanoma cells (1 × 105) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD- (250 μg) anti-CTLA-4 (250 μg), POM-1 (250 μg) alone or in various combinations as indicated on days 10, 13, 16, and 19. (E) Combination efficacy is IFN-γ- and CD8+ T cell-dependent. Groups (n = 6/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with RM-1 prostate carcinoma cells (5 × 104) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD1 (250 μg) or anti-CD39/anti-PD1 (200 μg/250 μg) on days 6, 9, 12, and 15. Some groups of mice were also treated i.p. with either cIg (100 μg), anti-asGM1 (50 μg) anti-CD8β (100 μg) or anti-mIFN-γ (250 μg) on days 5, 6 and 13. Tumor sizes (mm2) were measured at the indicated time points and presented as mean ± SEM. Significant differences between the treatment groups were determined by a two-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test (* P < 0.05, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001). (F,G) Groups (n = 5-6/group) of WT mice were injected s.c. with RM-1 prostate carcinoma cells (5 × 104) on day 0 and treated i.p with cIg (200 μg), anti-CD39 (200 μg), anti-PD1 (250 μg), anti-CD39/anti-PD1 (200 μg;250 μg) on days 6, 9, and 12. The tumors were collected on day 14, 48 h after the third dose, for TIL analysis by flow cytometry. (F) Graphs showing the frequencies of immune cell subsets in RM-1 tumors 2 days post the third injection of the indicated mAbs. (G) Representative FACS plots showing increased CD8+ T cell infiltration in RM-1 tumors on day 14, 2 days post the third anti-CD39/anti-PD1 mAb treatment. All experiments were performed once unless indicated. Significant differences in percentage between the selected cell populations were determined by one-way ANOVA, followed by Tukey's multiple comparison test (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, **** P < 0.0001).