Figure 3.
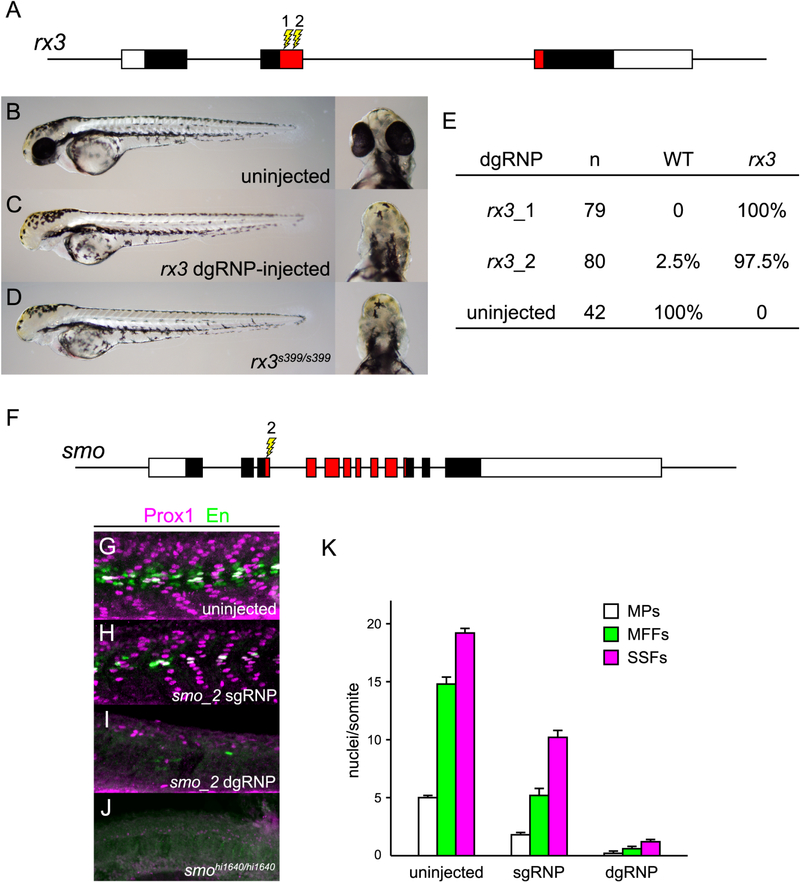
dgRNPs can produce accurate phenocopies of null mutants. (A–E) F0 embryos that develop from WT eggs injected with rx3 dgRNPs phenotypically resemble null rx3 mutants. (A) Two dgRNPs were designed to target sites (lightning bolts) within the region of rx3 exon 2 that encodes the DNA binding domain of the Rx3 transcription factor (red-shaded exon sequences). (B–E) Nearly all embryos injected with dgRNP complexes targeting either sites rx3_1 or rx3_2 lacked eyes and were indistinguishable from homozygous null mutants. (F–K) Injection of dgRNP complexes targeting smoothened (smo) produces F0 embryos that phenotypically resemble null smo mutants. (F) gRNPs were designed to target site smo_2 (lightning bolt) within the 5’ portion of the region that encodes the ‘Frizzled-domain’ of Smoothened (red-shaded exon sequences). (G–K) Development of three distinguishable types of muscle fibers is dependent on Sonic hedgehog signaling and Smoothened activity. Nuclei of Slow Muscle Pioneer Cells (MPs) express both the Prox1 and Engrailed (En) transcription factors, whereas Medial Fast Fibers (MFFs) only express En, and Superficial Slow Fibers (SSFs) only express Prox1. Shh-dependent muscle fiber nuclei, marked by Prox1 (magenta) and/or En (green) expression, were visualized following immunostaining of (G) uninjected, (H) smo_2 sgRNP-injected, or (I) smo_2 dgRNP-injected WT embryos, or (J) smohi1640 null mutant embryos. (K) The presence of Shh-dependent muscle fibers was determined by analysis of the nuclear staining in a standard set of five trunk somites in each embryo. The average numbers of Shh-dependent muscle fiber nuclei per somite for each embryo is plotted (uninjected (n=6), smo_2 sgRNP-injected (n=5), smo_2 dgRNP-injected (n=6)). See also Figure S3.