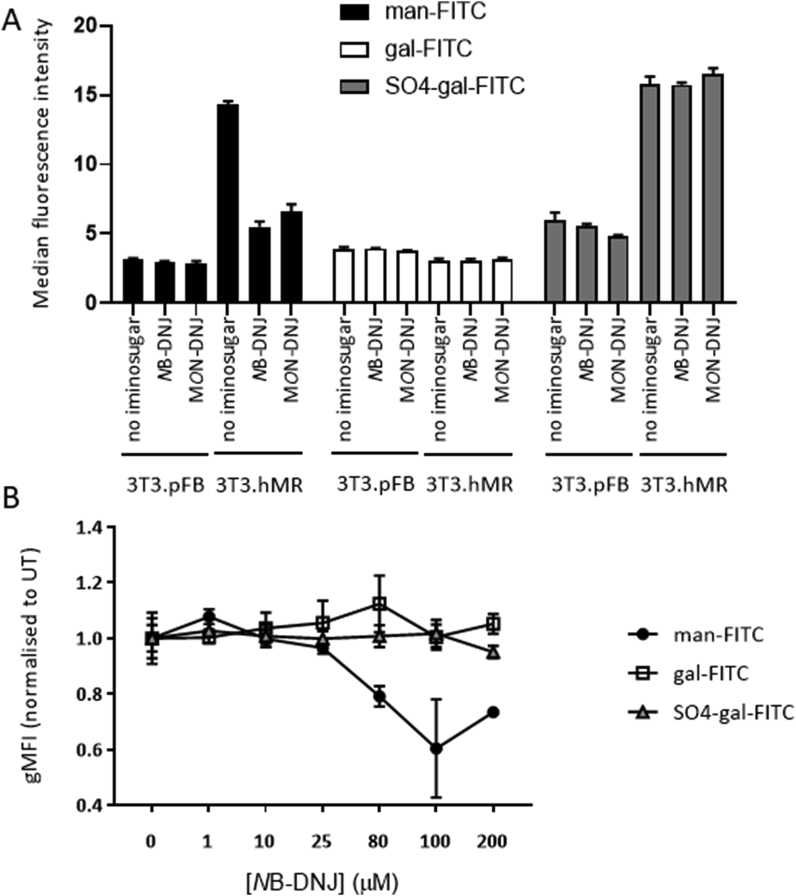
Fig. 1.
Iminosugars specifically reduce MR association with a CRD ligand. 3T3.hMR and 3T3.pFB were grown in the presence of NB-DNJ or MON-DNJ, washed, then incubated for 2 h at 37 °C with 5 μg/ml FITC-labelled sugar ligands (α-D-mannose-PAA-FITC (man-FITC), α-D-galactose-PAA-FITC (gal-FITC) or β-D-galactose-3-sulfate-PAA-FITC (SO4-gal-FITC) (GlycoTec)). The mannosylated ligand, man-FITC, is a specific endocytic tracer for ligands of the carbohydrate recognition domains (CRD) of the MR which bind mannose, fucose, and N-acetylglucosamine (Pontow et al., 1992); the sulphated galactose ligand, SO4-gal-FITC, is specifically bound by the cysteine-rich domain of the MR; while the galactosylated ligand, gal-FITC, shows background binding levels as it is not bound specifically by any domains of the MR. This assay measured associated ligand which was either bound or taken up into the cells as unbound ligands were washed away before association of FITC-labelled sugar with the cell was assessed by flow cytometry. (A) Single representative experiment showing growth of 3T3.pFB and 3T3.hMR cells for 2 days with 100 μM NB-DNJ or 25 μM MON-DNJ before assessing binding and uptake of FITC-sugar ligands, performed in triplicate. Background levels of association of each FITC-sugar to 3T3. pFB cells are shown. (B) Ligand binding to 3T3.hMR cells grown for 2 days in the presence of a titration of NB-DNJ, gMFI for each ligand normalised to levels bound in the absence of NB-DNJ, pooled data from 5 experiments, each performed in triplicate, mean±SD are shown.