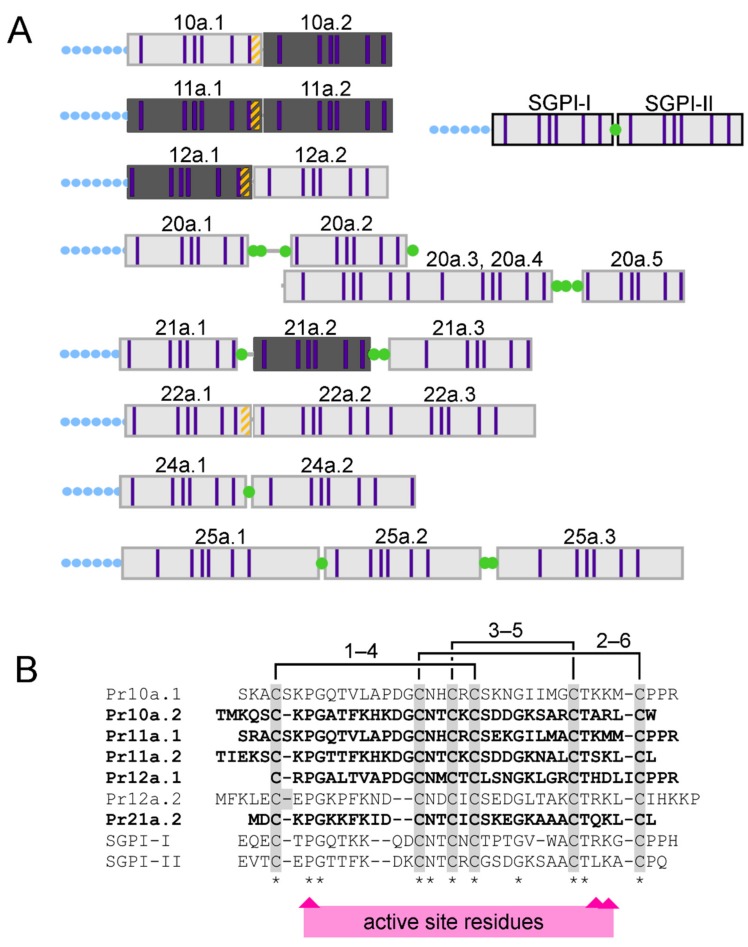
Figure 2.
Processing of pacifastin venom peptides. (A) Domain architecture of pacifastin precursors with Schistocerca gregaria protease inhibitors I and II (SGPI-I and SGPI-II) for comparison. Green dots indicate dibasic sites similar to those cleaved during SGPI processing; orange stripes denote Pro-Pro-Arg sites that we found are cleavage sites for proteolytic processing of Platymeris rhadamanthus pacifastin; blue-dotted lines indicate secretion signal sequences; and purple bars denote cysteine residues. (B) Alignment of Platymeris rhadamanthus venom pacifastins with SGPI peptides. The disulfide connectivity of SGPI peptides is shown above the sequences. Residues critical for inhibition of serine proteases by SGPI peptides are indicated below the sequence alignment. Darker-shaded peptides in panel A, and sequences in bold in panel B, were detected in their mature form in MS analysis of untrypsinised venom samples.