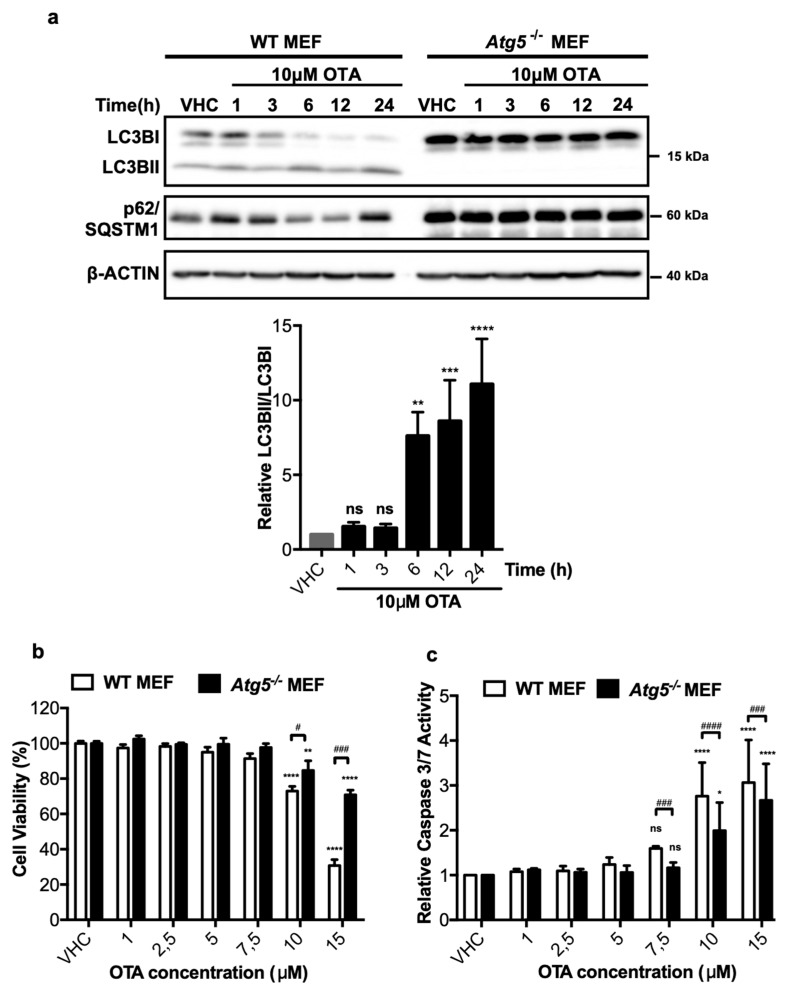
Figure 2.
OTA activates autophagy in mouse embryonic fibroblast (MEF) cells, and wild-type (WT) MEF cells are more prone to death and apoptosis than autophagy-deficient Atg5-/- MEF cells. (a) MEF cells were treated with 0.1% v/v Et-OH (VHC) for 24 h or OTA (10 µM) for indicated time periods. LC3B and p62/SQSTM1 protein levels were detected with specific antibodies. β-ACTIN was used as loading control. Blots are representative of three independent experiments. The images were obtained from the same or parallel blots of identical samples. (b) Cell viability and (c) apoptotic responses were observed in WT and Atg5-/- MEF cells upon OTA exposure. MEF cells were treated with OTA at indicated concentrations or vehicle (VHC) (0.1% v/v Et-OH) for 24 h. XTT Cell proliferation kit II and caspase 3/7 assays were used to investigate cell viability and apoptotic response, respectively. Cell viability was expressed as the percent cell viability relative to the control (100%). Caspase 3/7 activity was expressed as relative to VHC control (fold change). (ns: Nonsignificant, * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001 *in group comparisons with VHC; ns: Nonsignificant, # p < 0.05, ### p < 0.001, #### p < 0.0001, # comparison of groups (WT and Atg5-/- MEF)).