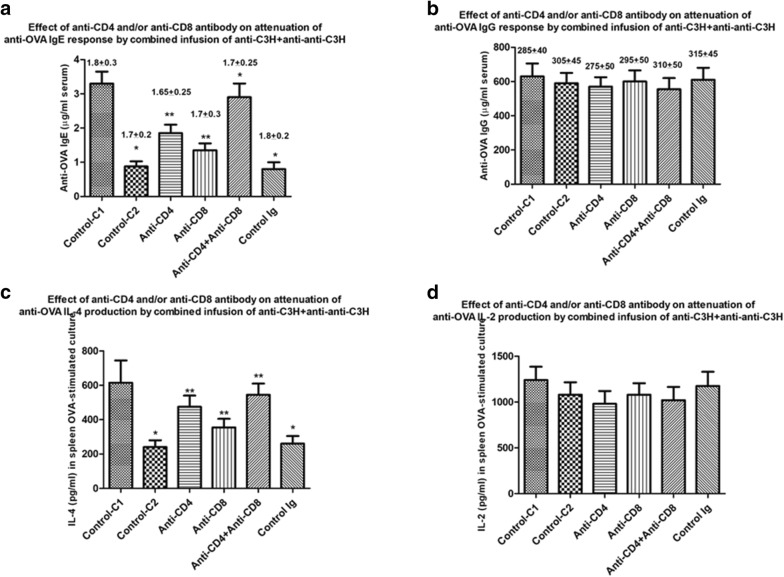
Fig. 7.
Amelioration by T depletion of attenuation of OVA-specific IgE and OVA-induced IL-4 production (a, c) but not IgG or OVA-induced IL-2 production (b, d) in groups of 8 BALB/c mice pre-immunized with OVA in alum (see text and “Materials and methods”), and subsequently receiving 5 weekly treatments with combined mouse immune Ig (anti-C3H) and anti-idiotype Ig (anti–anti-C3H). A control group (Control C1) received no further treatment after OVA immunization. Subgroups of 7 mice/group received either no further treatment besides the 5 combined mouse Ig treatments (Control C2), or treatment with CD4 or CD8 depleting antibodies, or both, at the 1st, 3rd and 5th Ig treatments (see Fig. 6). An additional control group received normal mouse Ig (Control Ig). Data show mean ± SD of Ig levels in serum in mice receiving a final boost of OVA in alum 7 days after the final immunoglobulin treatment and sacrificed 10 days later, or of cytokines in 72 h cultures of splenocytes from mice at sacrifice. Data in parentheses above each bar indicate the OVA-specific serum IgE or IgG levels in mice immediately after sensitization and before commencing treatment with anti-C3H immune Ig and/or anti–anti-C3H Ig. *p < 0.05 compared with Control C1. **p < 0.05 compared with Control C2