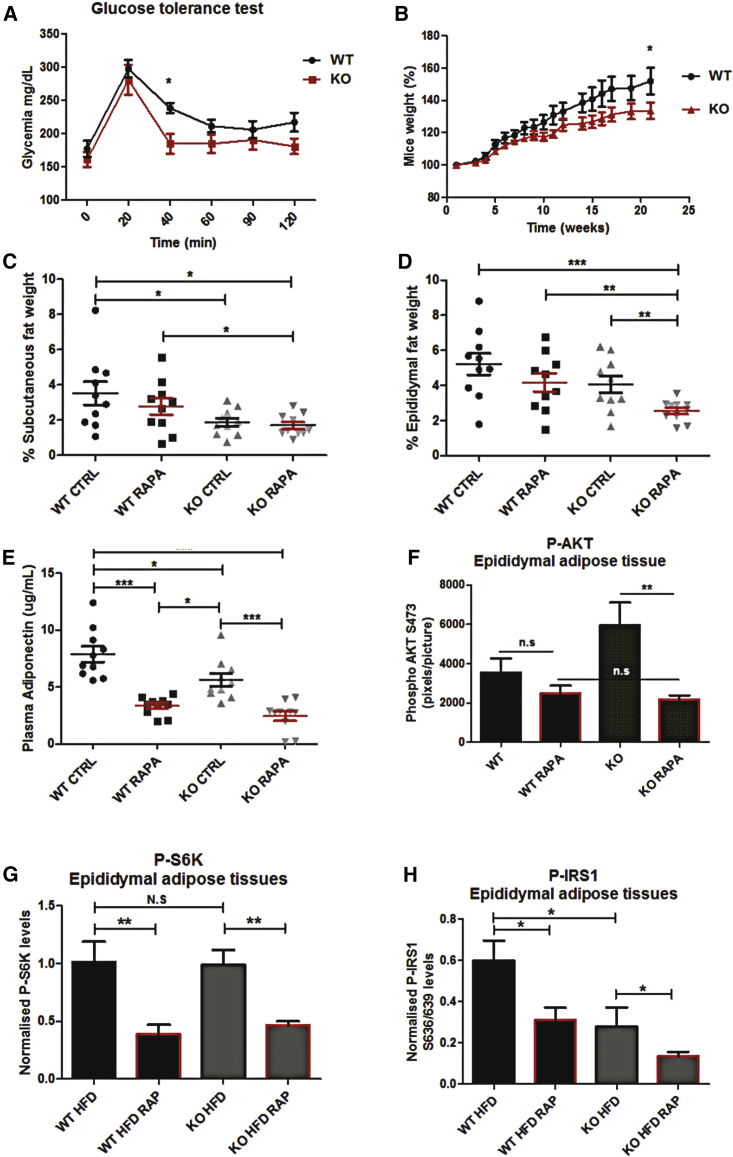
Figure 6.
DRAM1-Null Mice Are Less Prone to HFD-Induced Glucose Intolerance
(A) Glucose tolerance test was performed on mice fed a high-fat diet for 22 weeks. Blood glucose levels were measured at different time points following glucose administration (10 mice per group).
(B) Mouse weights were measured weekly during the course of the HFD experiment. Results are mean ± SEM for each time point (10 mice per group).
(C and D) Subcutaneous (C) and epididymal adipose tissues (D) were weighed at the end of the HFD experiment.
(E) Plasma adiponectin levels were measured for each mouse using ELISA.
(F) AKT activation levels in epididymal adipose tissues were evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) staining for phospho-AKT S473. Quantifications of at least 5 different mouse adipose tissues per group (5 pictures per mouse) were performed using Adobe Photoshop CS5.1 software.
(G and H) S6 kinase activation (G) and S636/639 IRS1 phosphorylation (H) in epididymal adipose tissues were evaluated by western blots for phospho-S6 kinase and phospho-S636/639 IRS1. Quantifications of 10 different mouse adipose tissues per group were performed using ImageJ. Where indicated, rapamycin (RAPA) was administrated (4 mg/kg) by intraperitoneal injection twice a week for the duration of the experiment.
All data are mean ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. n.s., non-significant.
See also Figure S6.