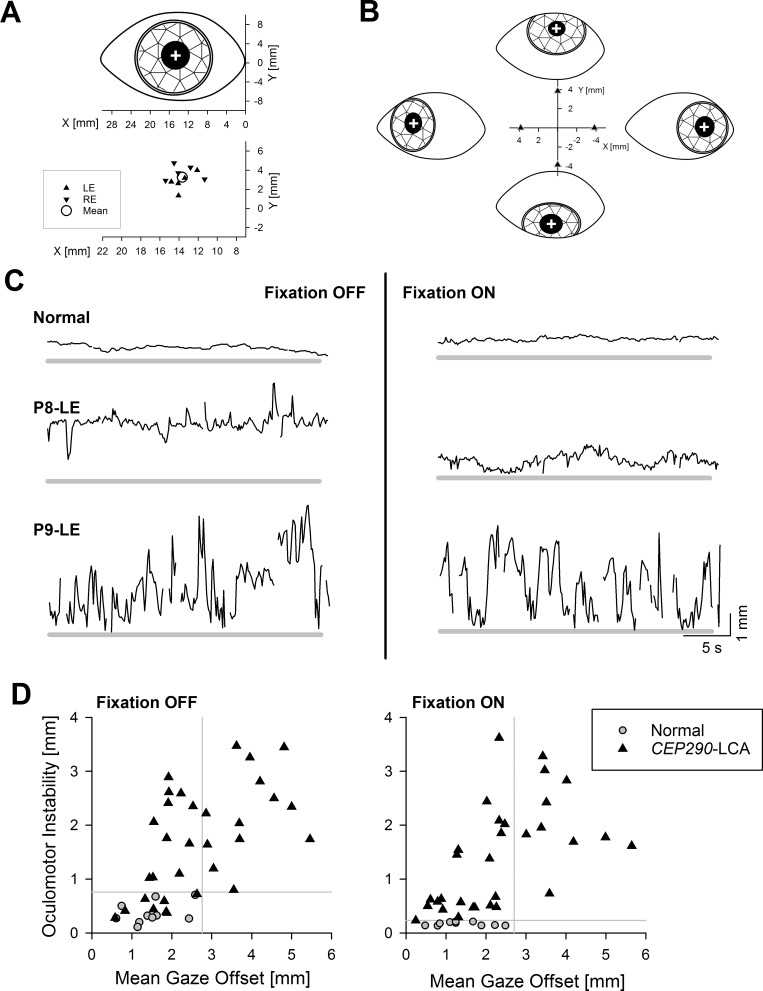
Figure 2.
Spectrum of oculomotor features in CEP290-LCA. (A) Upper: Schematic representation of the coordinate system centered at the medial (nasal) canthus and the center of pupil (white cross) at primary gaze. Lower: Individual data from left (LE) and right (RE) eyes of all normal subjects at primary gaze. Mean value is also shown (circle). (B) Schematic representation of eyes fixating 30° eccentric along the four cardinal directions, and relative offsets of the center of pupil measured from the primary gaze locus. (C) Chart records showing the radial offset of the center of pupil from the mean normal primary gaze locus (thick gray line) during a 30-second-long recording epoch in a representative normal subject and two CEP290-LCA eyes. Two records shown are with (right column) and without (left column) fixation. (D) Oculomotor instability plotted against mean gaze offset in individual CEP290-LCA eyes (triangles; n = 32 eyes of 16 patients) recorded with and without fixation. Equivalent results from normal eyes are also shown (gray circles). Gray lines demarcate the upper (mean + 2 SD) limits of normal for each parameter. Reprinted with permission from Jacobson SG, Cideciyan AV, Sumaroka A, et al. Outcome measures for clinical trials of Leber congenital amaurosis caused by the intronic mutation in the CEP290 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58:2609–2622. © 2017 The Authors. Published by ARVO.