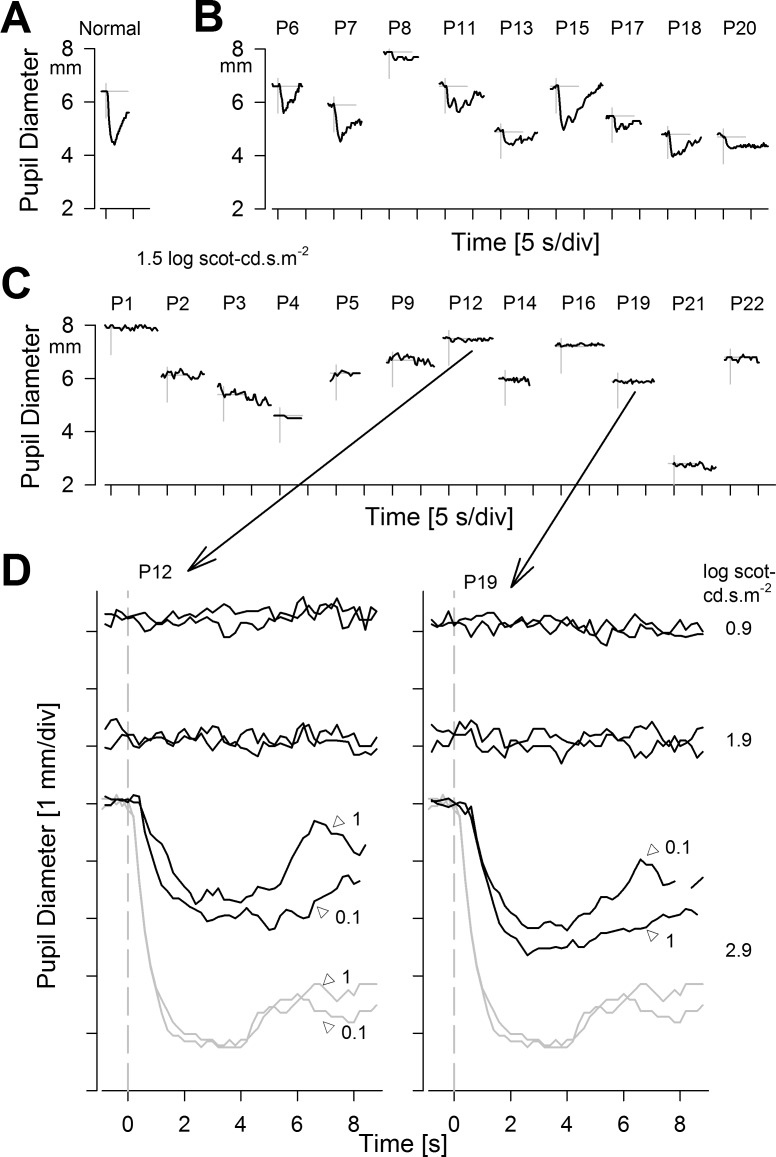
Figure 6.
Pupillary light reflexes in CEP290-LCA. (A–C) Dynamics of pupil constriction in the dark to a 0.1-second-duration achromatic bright standard stimulus (1.5 log scot-cd.s.m−2) in a representative normal (A), CEP290-LCA patients grouped into those with detectable responses (B), and those without (C). (A–C) Modified from Jacobson SG, Cideciyan AV, Sumaroka A, et al. Outcome measures for clinical trials of Leber congenital amaurosis caused by the intronic mutation in the CEP290 gene. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58:2609–2622. © 2017 The Authors. Published by ARVO. (D) Use of higher stimulus luminance range in two of the eyes with no pupillary response to standard stimuli. Notably, 0.9 and 1.9 log scot-cd.s.m−2 stimuli do not evoke responses, whereas 2.9 log scot-cd.s.m−2 stimuli evoke definite responses that are smaller and slower than normal. Similarity of responses with 0.1- and 1-second-long stimuli suggests reciprocity between stimulus luminance and duration. (D) Modified from Charng J, Jacobson SG, Heon E, et al. Pupillary light reflexes in severe photoreceptor blindness isolate the melanopic component of intrinsically photosensitive retinal ganglion cells. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2017;58:3215–3224. © 2017 The Authors. Published by ARVO.