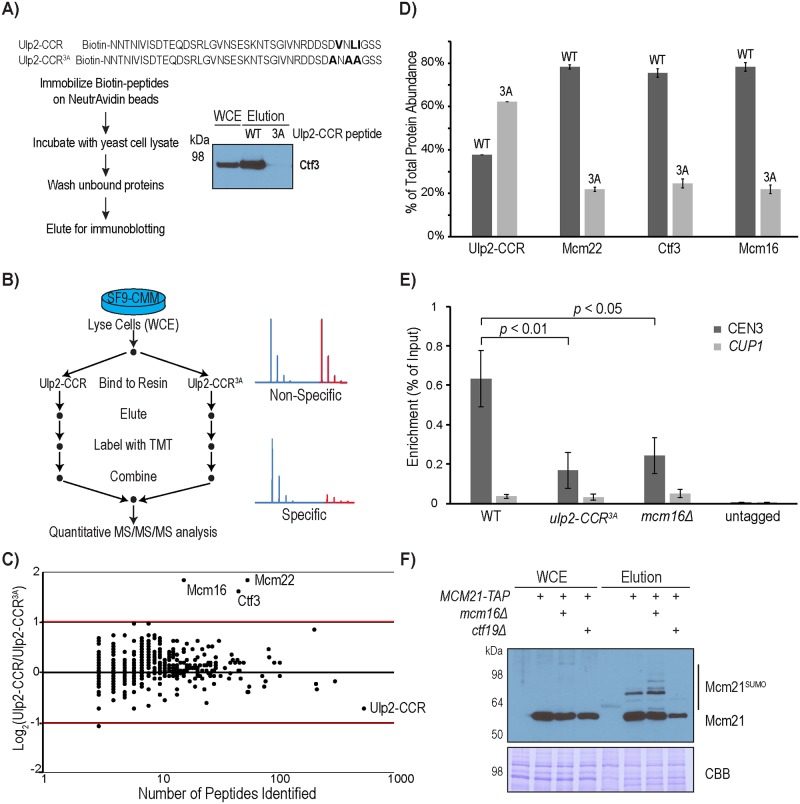
Fig 4. Ulp2’s CCR directly binds to the CMM complex.
A) Experimental schematic and Western blot analysis for detecting the binding of a synthetic Ulp2-CCR peptide with Ctf3 in yeast cell extract. B) Experimental design to use TMT-based quantitative MS to compare the binding proteins of Ulp2’s CCR, purified using SF9 cells expressing the CMM complex. C) Log2 ratios of proteins associating with Ulp2-CCR versus Ulp2-CCR3A, identified by MS, are plotted on the Y-axis, while the number of peptides identified for each protein is plotted on the X-axis. D) Quantification of the relative abundance of Mcm16, Ctf3, Mcm22 and Ulp2-CCR is shown in Figure 4C. Error bars were calculated based on the standard error of the mean of TMT reporter ions found in multiple peptides of each protein. E) ChIP-qPCR analysis to measure the association of Ulp2 to the Centromere-III revealed a partial role for Ulp2’s CCR and Mcm16. The p-values indicate statistically significant differences of Ulp2-TAF with Ulp2-CCR3A-TAF and mcm16Δ using a two-tailed Student’s t-test. F) Effect of mcm16Δ and ctf19Δ on sumoylated Mcm21, which was purified using the Ulp1-C580S affinity resin (see Fig 2).