Fig. 3. TNFα depletion at the time of C. neo infection altered lung DC H3K4me3 at crucial DC1 genes.
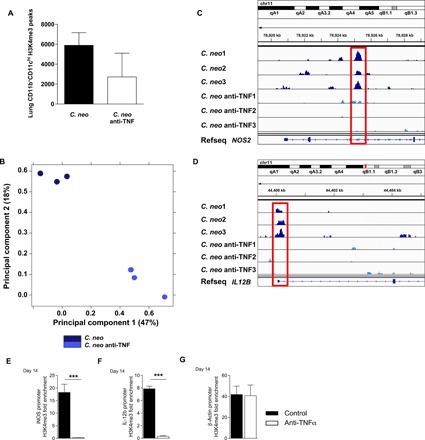
CBA/J mice were infected with C. neo intratracheally, and half were injected intraperitoneally with anti-TNFα antibodies on day 0 and were harvested at 14 dpi. (A) Total CD11b+CD11chi lung DC H3K4me3 peaks. Box represents mean; bar represents SEM. (B) Principal components analysis of total CD11b+CD11chi lung DC H3K4me3 normalized read counts. The principal components are based on H3K4me3 binding site location and affinity for those locations. C. neo–infected cells cluster together along principal components 1 and 2, and C. neo anti-TNF–treated cells cluster together along principal components 1 and 2 with significant separation from each other. (C) C. neo samples have an enriched H3K4me3 peak inside the DC1 gene NOS2 that is absent in C. neo anti-TNF samples. (D) C. neo samples have an H3K4me3 peak at the promoter site of the DC1 gene IL12B, which is absent in the C. neo anti-TNF samples. Input-subtracted H3K4me3 bigwig peak files were visualized using the Integrated Genomics Viewer (IGV). C. neo: C. neoformans infected; C. neo anti-TNF: C. neoformans infected, anti-TNF antibody treated; 1, 2, 3: replicates. (D to F) ChIP-qPCR showed DC1 gene promoter enrichment for H3K4me3. CD11c+ cells were harvested from the lungs of infected control and anti-TNFα mice at day 14, and ChIP was performed using H3K4me3 antibodies. qPCR was performed on recovered DNA for promoter regions of iNOS (D), IL-12b (E), and β-actin (F). n = 3 replicates per group pooled from three separate experiments of 20 million DCs. ***P < 0.001 between the indicated samples; no pairing was performed.
