Fig. 2. BAZ1B KD is responsible for transcriptional alterations in NC-related pathways.
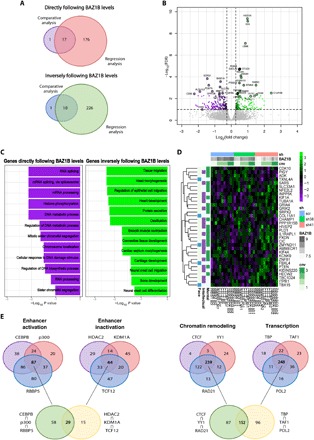
(A) Overlap between genes directly or inversely following BAZ1B levels identified in the pairwise comparative analysis (scr versus shBAZ1B) and in the regression analysis on BAZ1B-level sensitive genes on iPSC-derived NCSCs (FDR < 0.1). (B) Volcano plot reporting DEGs identified in the RNA-seq analysis on iPSC-derived NCSCs [fold change (FC) > 1.25; FDR < 0.1]. (C) Top most specific enrichments for GO biological processes among the DEGs in the RNA-seq analysis on iPSC-derived NCSCs. (D) Heat map representing DEGs that are dysregulated in genetic disorders involving mental retardation (“Mental”), intellectual disability (“Intellectual”), and/or facial dysmorphisms (“Face”) according to OMIM database classification. cnv, copy number variant. (E) Putative regulators of genes that follow BAZ1B levels identified by a master regulator analysis. Regulators were divided in four different groups based on their main functions.
