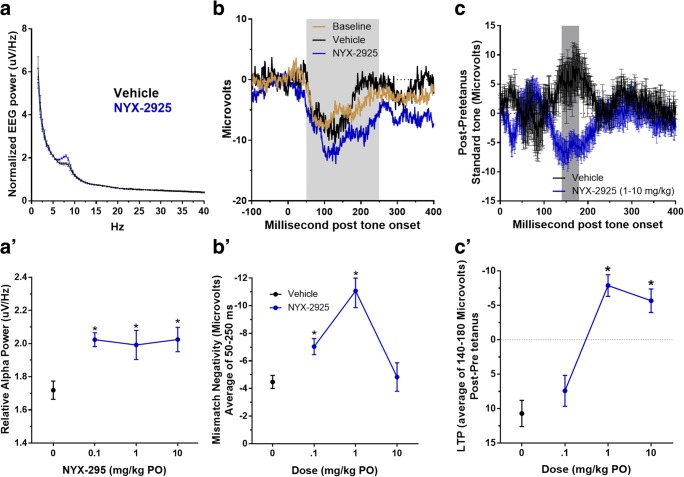
Fig. 1.
NYX-2925 enhances resting alpha power (qEEG), mismatch negativity (MMN), and auditory-induced long-term potentiation (aLTP). (A, A’) Average power spectral density plots showing that NYX-2925 (0.1, 1, 10 mg/kg PO) enhanced alpha power (7–8.5 Hz) compared with vehicle without affecting power in the other EEG bands (data not shown). (B, B’) Grand average MMN waveforms for showing that NYX-2925 (0.1, 1 mg/kg PO) enhanced MMN compared with vehicle from 50 to 250 ms after tone onset. (C, C’) Average post-pre tetanus waveforms show that NYX-2925 (1, 10 mg/kg PO) enhanced aLTP 140–180 ms after tone onset. This range was used given that this was the region in which the vehicle group showed the largest post-pre tetanus change. (B) LTP was enhanced in the 1 and 10 mg dose groups (p < .05). Using a similar methodology (Clapp et al. 2006), an NMDAR antagonist has been shown to inhibit sensory-induced LTP. Mean ± SEM. *p < .05 Bonferroni post hoc test vs. vehicle following a one-way ANOVA. n = 7–10 per group