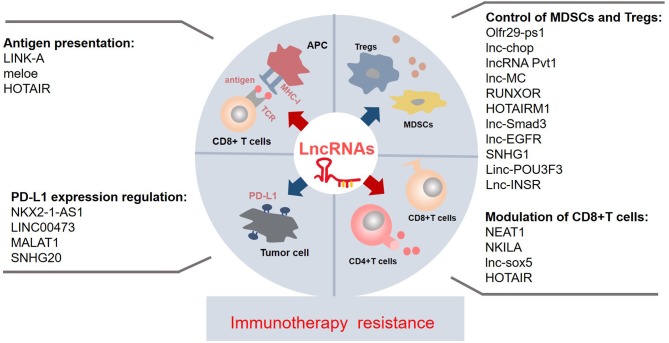
Figure 1.
The known immune-related lncRNAs may play a vital role in the immunotherapy resistance via regulating the immune components and environment at different levels and by a myriad of mechanisms. The suppressive antigen presentation, upregulated PD-L1 expression on the tumor, the dysfunctions of T cells, and accumulation of immunosuppressive cells contribute to the immunotherapy resistance. A few lncRNAs affect the process of antigen presentation; they impair/enhance the MHC-I function or produce specific antigens. Some lncRNAs regulate the PD-L1 expression on the tumor, especially upregulating the PD-L1 expression. Majority of lncRNAs control the recruitment and activity of MDSCs and Tregs; most of them are upregulated in the MDSCs and Tregs. Collectively, most of known immune-related lncRNAs may contribute to the immunotherapy resistance. lncRNAs, long non-coding RNAs; Tregs, regulatory T cells; MDSCs, myeloid-derived suppressor cells; APC, antigen-presenting cell; PD-L1, programmed cell death protein 1; TCR, T-cell receptor; MHC-I, major histocompatibility complex.