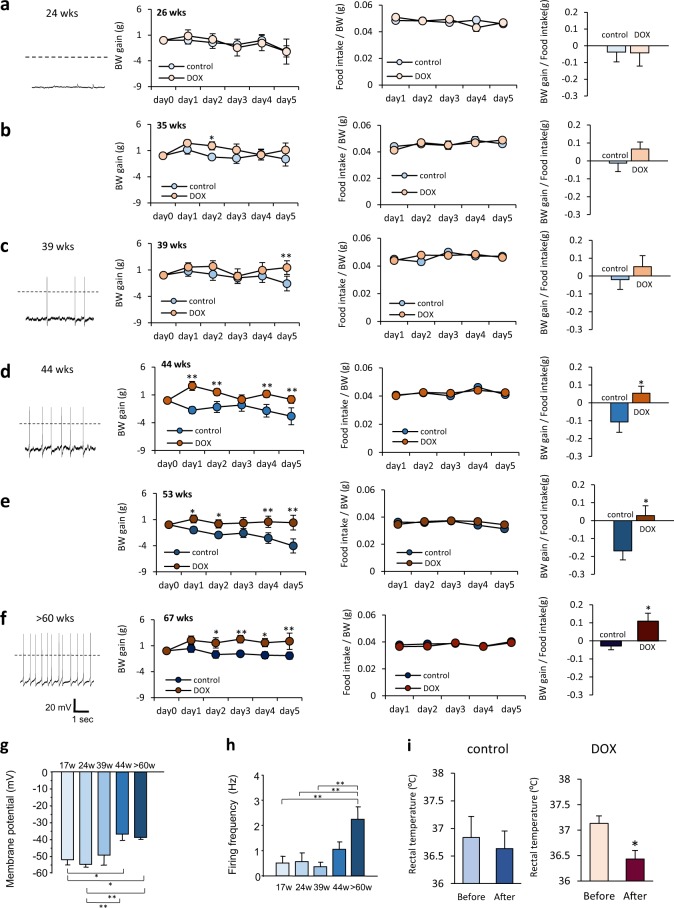
Figure 2.
Age-dependent effects of the reversible blockade of the synaptic transmission from the PVN to the DVC. (a–f) left: Representative recordings of the electrical activity of PVN neurons in the brain slices at ages 24 (n = 17) (a), 39 (n = 10) (c), 44 (n = 10) (d), and >60 (n = 13) weeks (f). Middle left and middle right: BW gain (middle left panel), food intake/BW (middle right panel) during intraperitoneal DOX injection at 26 weeks (BW gain, [F1, 70 = 0.117, P > 0.05]; food intake, [F1, 56 = 0.003, P > 0.05]) (n = 8, 8) (a), 35 weeks (BW gain, [F1, 70 = 7.633, P < 0.01]; food intake, [F1, 56 = 0.009, P > 0.05]) (n = 7, 9) (b), 39 weeks (BW gain, [F1, 75 = 7.779, P < 0.05]; food intake,[F1, 60 = 0.226, P > 0.05]) (n = 8, 9) (c), 44 weeks (BW gain, [F1, 65 = 41.042, P < 0.01]; food intake, [F1, 52 = 0.058, P > 0.05]) (n = 7, 8) (d), 53 weeks (BW gain, [F1, 75 = 31.798, P < 0.01]; food intake, [F1, 60 = 2.132, P > 0.05]) (n = 8, 9) (e), and 67 weeks old (BW gain, [F1, 30 = 25.738, P < 0.01]; food intake, [F1, 30 = 1.610, P > 0.05]) (n = 4, 4) (f). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Two-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. right panel: Food efficacy (average calculated from BW gain/food intake during DOX administration) at 26 (a), 35 (b), 39 (c), 44 (d), 53 (e), and 67 (f) weeks old. Unpaired t-test. (g,h) The membrane potential in the PVN neurons at 17, 24, 39, 44, and >60 weeks old. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. n = 9–15 (g). The firing frequency in the PVN neurons at 17, 24, 39, 44, and >60 weeks old. **P < 0.01, one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s multiple range test. n = 9–15 (h). (i) Rectal temperature before (Day 0) and after (Day 3) the saline (left panel, control) or DOX (right panel) injection. *P < 0.05, paired t-test. n = 3 each.