Figure 2.
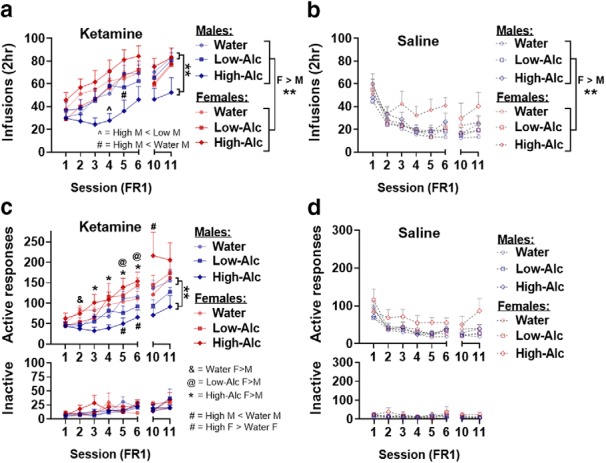
Ketamine acquisition under the FR1 schedule of reinforcement is reduced in high-alcohol intake male rats, but not female rats. a, b, Number of ketamine or saline infusions under an FR1 schedule of reinforcement during 2 h sessions in male and female rats, respectively. a, Infusions were significantly decreased in high-alcohol intake male rats (n = 8) in session 4 compared with low-alcohol intake rats (n = 8) and session 5 to water-intake rats (n = 11). Female rats self-administered more ketamine than males, and high-alcohol intake female rats were significantly higher than high-alcohol intake male rats for the final two FR1 sessions (SA sessions 10–11). b, No intake differences were observed in saline self-administering rats of either sex. c, d, Number of active and inactive responses during FR1 sessions in male and female rats. Responses include the number of nose pokes rewarded and unrewarded during the 20 s timeout period. c, High-alcohol intake male rats decreased active responses in session 5 compared with water-intake males and session 6 compared with low-alcohol intake males, and an overall reduction was observed during the final two FR1 sessions (SA sessions 10–11). Water-intake females (n = 11) showed a significant increase in active responses compared with males in session 2, while high-alcohol intake females (n = 7) displayed this sex difference from sessions 3 to 6 and low-alcohol (n = 8) from sessions 5 to 6. d, Intake did not affect responding in the saline groups. The *, #, @, &, ^ p < 0.05 symbols represent either within- or between-sex differences (indicated in a and c). Data are represented as the mean ± SEM infusions or responses for ketamine (0.5 mg/kg/infusion) or saline. Saline self-administration male and female rats with water intake (n = 11), low alcohol intake (n = 8), and high alcohol intake (n = 7). Low-alcohol intake female rats that self-administered ketamine (n = 8). **p < 0.01.
