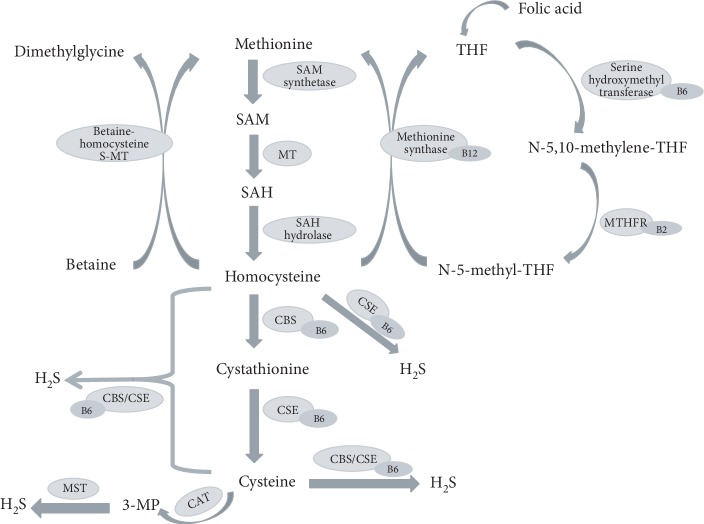
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the association between homocysteine and H2S. Homocysteine is biosynthesized from methionine by S-adenosylmethionine (SAM) synthetase, methyltransferase (MT), and S-adenosylhomocysteine (SAH) hydrolase in sequential steps. Homocysteine can be either remethylated to methionine through folate/vitamin B12-dependent or vitamin B12-independent mechanisms, or transsulfurated to cysteine under the catalysis of cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) and cystathionine γ-lyase (CSE) that requires vitamin B6 as an enzyme cofactor. Homocysteine and cysteine are substrates for H2S production, and the generation of H2S is catalyzed by CBS, CSE, and 3-mercaptopyruvate sulfurtransferase (MST). THF: tetrahydrofolate; 3-MP: 3-mercaptopyruvate; CAT: cysteine aminotransferase; MTHFR: N-5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase.