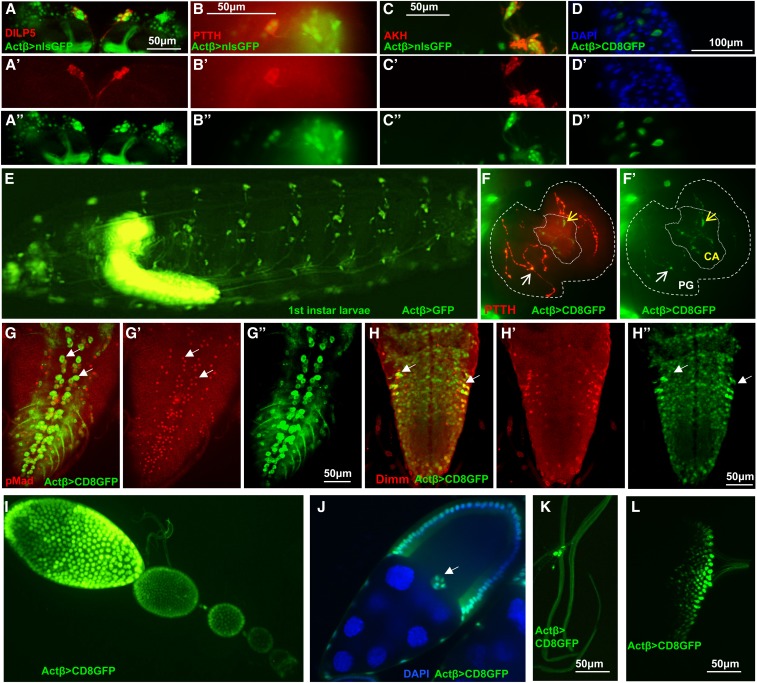
Figure 6.
Analysis of Actβ-GAL4 driver expression pattern (green) in L3 larvae and female ovaries. (A–A’’) Actβ-GAL4-2A2 is expressed in the insulin-producing cells in the central brain, marked with α-Dilp5 (red). (B–B’’) Actβ reporter is expressed in the cell bodies of PTTH neurons (α-PTTH, red) in the central brain. (C–C’’) Actβ reporter is expressed in Akh-producing (α-AKH, red) neurons. (D–D’’) Actβ-Gal4-driven GFP is expressed in midgut enteroendocrine cells (blue, DAPI). (E) An intact L1 larva, Actβ-Gal4-driven GFP is expressed in both the CNS and PNS. (F and F’) Actβ-Gal4-2A2-driven GFP is found in PTTH synaptic boutons (red) on the PG (thicker dotted line, white arrows) as well as unique boutons in the CA (finer dotted line, yellow arrows). (G–G”) Actβ reporter drives expression in the motor neurons (marked with α-pMad red) in the ventral nerve cord (white arrows highlight two individual motor neurons). (H–H”) Actβ reporter is expressed in neuroendocrine cells (α-DIMM, red) in the ventral nerve cord. (I and J) Actβ-Gal42A2-driven GFP is found in follicle cells and the border cells [white arrow in (J)] during egg development. (K) Actβ-Gal4-2A2-driven GFP is found in certain tracheal-associated cells (likely neuroendocrine Inka cells) and (L) in differentiating photoreceptor cells in the eye disc. ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, and **** P < 0.0001. CA, corpus allatum; ns, not significant; PG, prothoracic gland; PTTH, prothoracicotropic hormone.