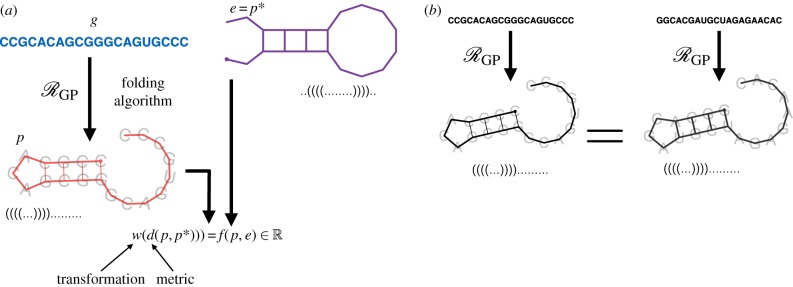
Figure 5.
The RNA folding model. (a) RNA folding as an evolutionary system . The GP-mapping takes a genotype g to a minimum free energy secondary structure p through an RNA folding algorithm (ViennaRNA [110]). The environment is specified as a target structure e = p* and fitness is determined as a transformation (w) of the distance (d) between a structure and this target. (b) Phenotypes/secondary structures are topologically defined, thus two RNA strands can fold into the same target structure. (Online version in colour.)