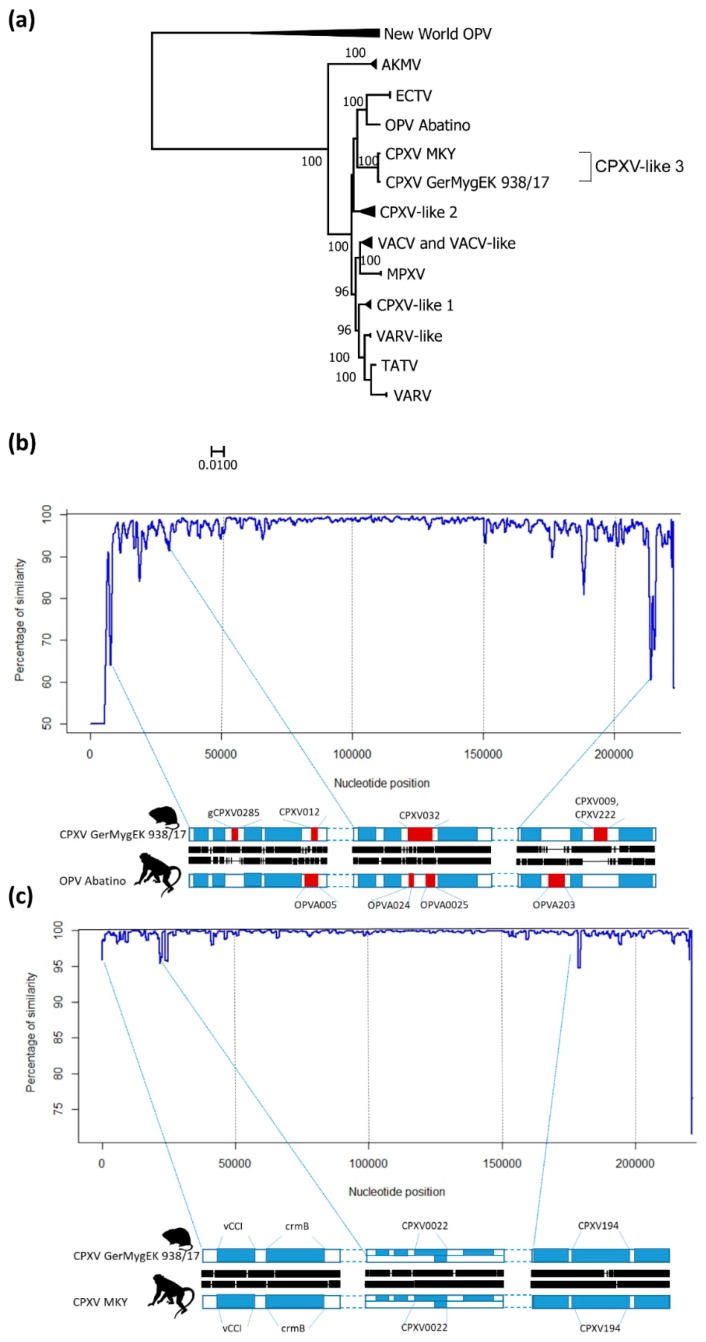
Figure 2.
Phylogenetic analysis and sequence similarity analyses of CPXV GerMygEK 938/17. (a) Phylogenetic tree using New World orthopoxviruses as outgroup. Clades where named after Franke et al., 2017 [16]. Only bootstrap supporting values over 70 are given at the supported nodes. Black triangles indicate compressed branches. (b) Similarity plot showing the sequence identity between CPXV GerMygEK 938/17 (query sequence, black line) to the reference sequences OPV Abatino (MH816996, blue line) along their full genomes. Three regions exhibiting prominent differences are detailed below as a zoom-in visualization. Gaps between black lines indicate gaps in the DNA sequence. (c) Similarity plot showing the sequence identity between CPXV GerMygEK 938/17 (query sequence, black line) to the reference sequences CPXV MKY (LT896721, blue line) along their full genomes. Alignment details of three genomic parts are depicted below. Open reading frames (ORFs) that are conserved in both genomes are colored in blue, while ORFs that are present in either one of the two genomes are colored in red. White areas represent intergenic regions.