Figure 2.
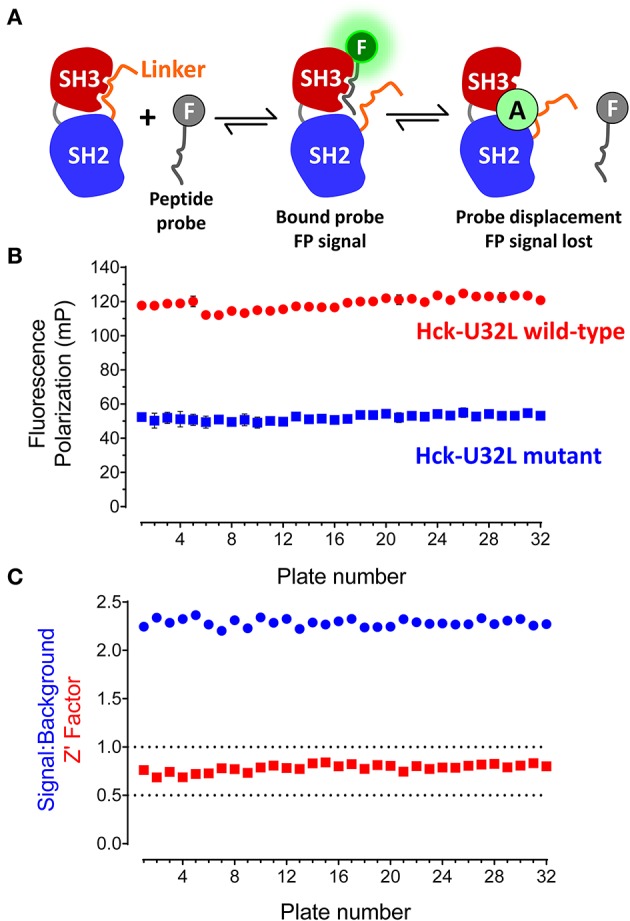
FP-based HTS assay for SH3-SH2 ligands. (A) FP assay principle. The FP assay for Hck combines a recombinant N-terminal unique-SH3-SH2-linker (“U32L”) protein with an SH3-binding probe peptide labeled with fluorescein (F). Probe peptide binding to the SH3 domain in the target protein results in an FP signal. Small molecule allosteric modulators (A) may bind to the SH3 domain and block probe peptide binding directly as shown or stabilize SH3:linker interaction, making the SH3 domain inaccessible to the probe peptide (not shown). In either case, small molecule binding reduces the FP signal. The N-terminal region is not illustrated for clarity. (B) FP assay performance under robotic HTS conditions. The FP assay was automated and used to screen a 10,000-compound library using 32 × 384-well plates. Each plate had 32 wells of the target protein with DMSO only (Hck-U32L wild-type) and 32 wells of a protein with an inactivating mutation in the SH3 domain that cannot bind the probe as the negative control (Hck-U32L mutant). Average FP (mP) values from the control wells are shown ± S.D.; note that some error bars are smaller than the size of the corresponding data point. (C) Screening statistics. Signal-to-background ratios and Z'-factor coefficients calculated from control wells on each assay plate are shown.
