Figure 2.
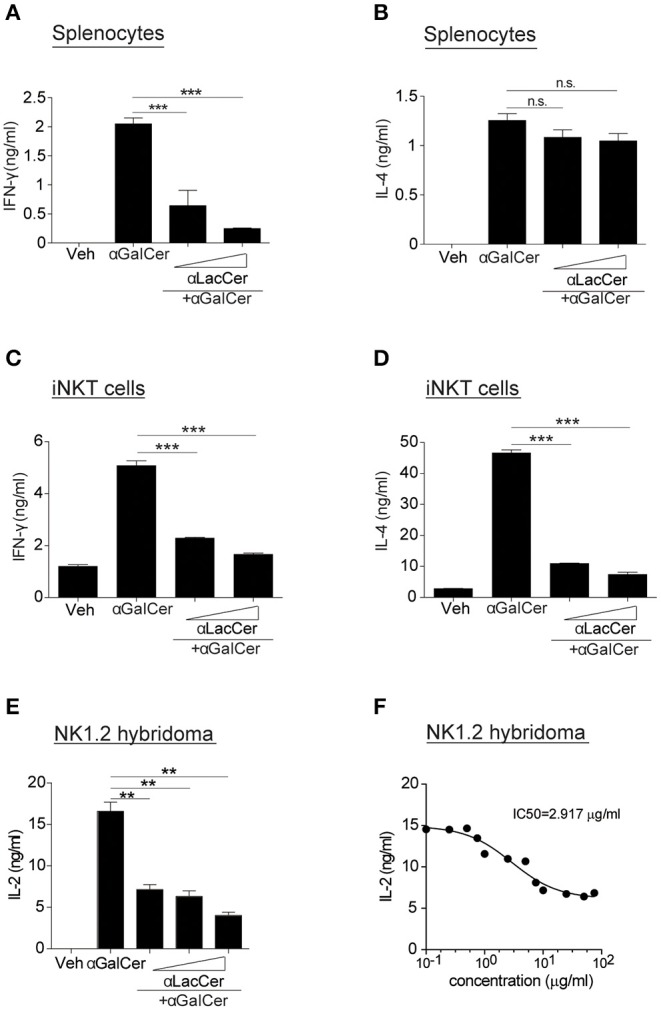
α-LacCer suppresses α-GalCer-induced cytokine production in vitro. (A,B) Splenocytes from BALB/c mice were stimulated with 100 ng/ml α-GalCer in the presence or absence of α-LacCer (5 or 20 μg/ml) for 48 h. The levels of IFN-γ (A) and IL-4 (B) in the supernatant were measured (n = 3). (C,D) Sorted mouse iNKT cells were co-cultured with irradiated BMDCs and stimulated with α-GalCer (100 ng/ml) in the presence or absence of α-LacCer (5 or 20 μg/ml) for 48 h. The levels of IFN-γ (C) and IL-4 (D) in the supernatant were measured (n = 3). (E) NK1.2 cells in co-culture with A20-CD1d cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml α-GalCer in the presence or absence of α-LacCer (100, 1,000, or 10,000 ng/ml) for 48 h. The level of IL-2 in supernatants was measured (n = 3). (F) NK1.2 cells in co-culture with A20-CD1d cells were stimulated with 100 ng/ml α-GalCer in the presence of incremental levels of α-LacCer (0.1–100 μg/ml) for 48 h. The level of IL-2 in supernatants was measured (n = 4), and GraphPad Prism was utilized for calculating the IC50. Data are representative of three independent experiments and presented as means ± s.e.m. [n.s., not significant; **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001; Student's t-test (A–F)].
