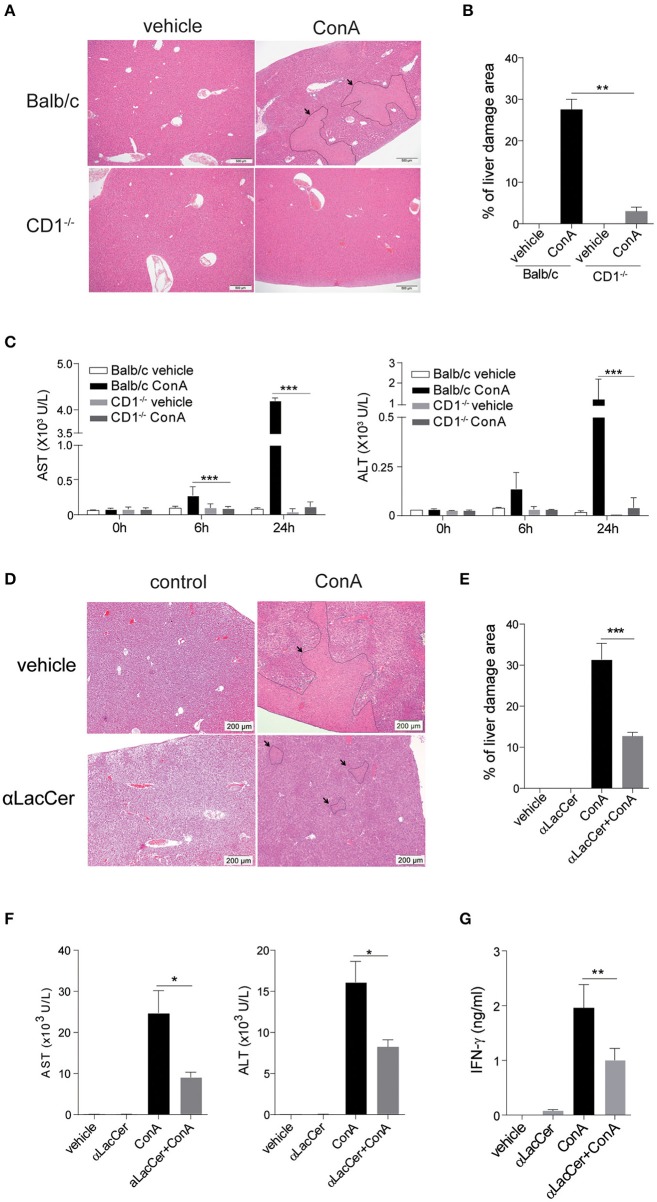
Figure 5.
α-LacCer protects against ConA-induced liver injury. (A–C) ConA was injected intravenously (25 mg/kg) into BALB/c (n = 3) or CD1d−/− mice (n = 3). Sera were collected at 0, 6, and 24 h post-injection, and mice were sacrificed at 24 h post-injection. (A) H&E stained liver sections (Scale bar = 500 μm). (B) Percentage of liver damage area. (C) Serum levels of ALT and AST. (D–G) BALB/c mice were first pre-treated intraperitoneally with α-LacCer (5 μg/ml) for 24 h and followed by ConA (25 mg/kg; i.v.) administration. Sera and livers were harvested 24 h post-ConA treatment. (D) H&E stained liver sections (Scale bar = 200 μm). (E) Percentage of liver damage area (n = 3). (F) Serum levels of AST and ALT (n = 4). (G) The serum IFN-γ level measured by ELISA (n = 4). Data are representative of three independent experiments and are presented as means ± s.e.m. [*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001; Student's t-test (B,C,E–G)].