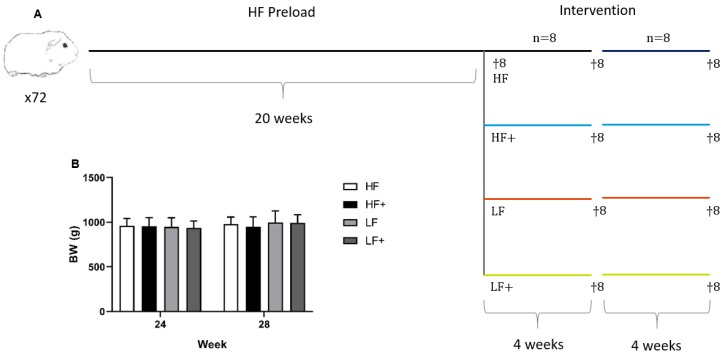
Figure 1.
Study overview and body weights of animals. (A) Seventy-two guinea pigs were preloaded on a high-fat diet for 20 weeks. Prior to intervention, eight animals were randomly selected for euthanasia, serving as baseline values. The remaining guinea pigs were weight stratified into the following groups (n = 16): HF, continuing on the high-fat diet (20%, 0.35% cholesterol, and 15% sucrose); HF+, receiving high-fat diet with atorvastatin and vitamin E (20 mg/kg feed atorvastatin and 375 mg/kg feed all-rac vitamin E, for a guinea pig corresponding to a daily intake of 1 mg/kg atorvastatin and 800 IU vitamin E); LF, receiving a standard guinea pig chow diet (4% fat, 0% cholesterol, and 0% sucrose); LF+, receiving a standard guinea pig chow diet with atorvastatin and vitamin E (20 mg/kg feed atorvastatin and 375 mg/kg feed vitamin E). After four weeks of intervention, eight randomly chosen guinea pigs, from each group, were euthanized, leaving the remaining eight animals for another four weeks of intervention before termination. (B) No differences were recorded in body weight (BW) through the study.