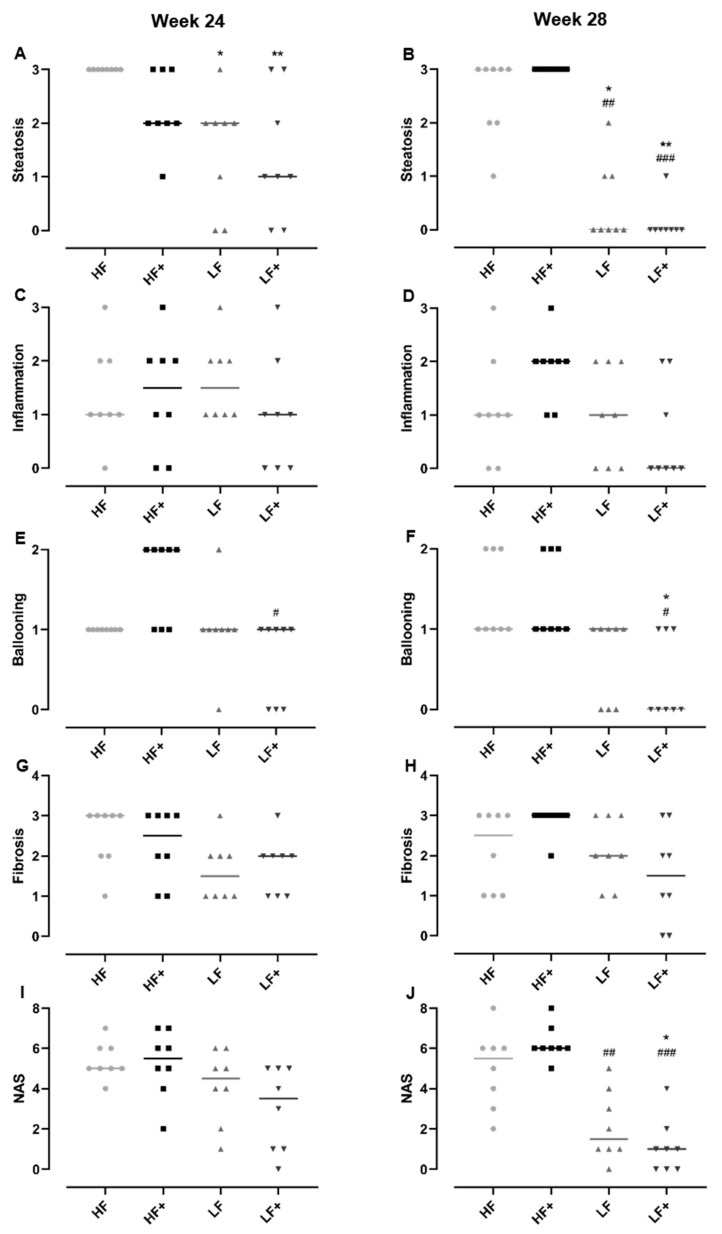
Figure 4.
Histopathological scoring by the NAFLD activity scoring system and evaluation of disease severity. (A,B) Dietary intervention (LF) and dietary intervention combined with atorvastatin and vitamin E (LF+) reduced hepatic steatosis compared to HF (after 24 and 28 weeks) and HF+ (after 28 weeks), with increasing significance in the LF+ group. (C,D) No significant effect was observed after 24 and 28 weeks in the inflammatory score. However, a trend towards reduction in the LF+ group compared with HF and HF+ was seen. (E,F) A significant reduced ballooning score in the LF+ group compared with HF+ were detected after 24 and 28 weeks. Furthermore, after 28 weeks LF+ were also significantly reduced compared with the HF group. The LF group displayed no effect compared to HF and HF+. (G,H) After 28 weeks, the fibrosis score of the LF+ appeared to be decreasing compared with HF and HF+. However, no significant effects were detected. (I,J) No significant differences in the NAS were detected after 24 weeks. After 28 weeks, both LF and LF+ were significantly reduced compared with HF+, while LF+ were also significantly reduced compared with HF, with no guinea pig reaching the minimum score of 5. Data are presented as individual values with medians. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, compared to HF; # p < 0.05, ## p < 0.01, ### p < 0.001, compared to HF+.