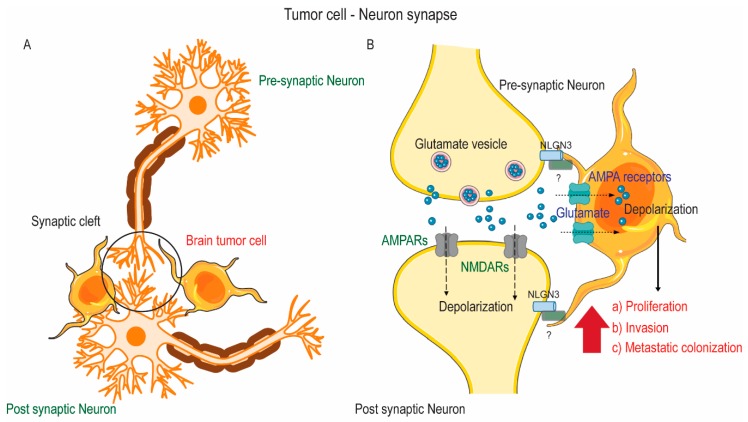
Figure 2.
Glioma—Neuron crosstalk. (A) Glioma cells form synaptic connections with neurons at glutamatergic synapses. (B) Brain tumor cells upregulate glutamate receptor (including AMPA family of receptors) and post-synaptic structural genes (including neuroligin-3) to establish synaptic connections. Electrochemical stimulation of neurons results in release of glutamate in the synaptic cleft, which rapidly depolarizes glioma. This drives an influx of Ca2+ ions, which promotes tumor cell proliferation and increases invasiveness and metastatic colonization of glioma cells. Abbreviations: AMPA, α-amino-3-hydroxy-5methyl-4-isoxazole propionic acid; NMDA, N-methyl-D-aspartate; NLGN-3, Neuroligin-3.