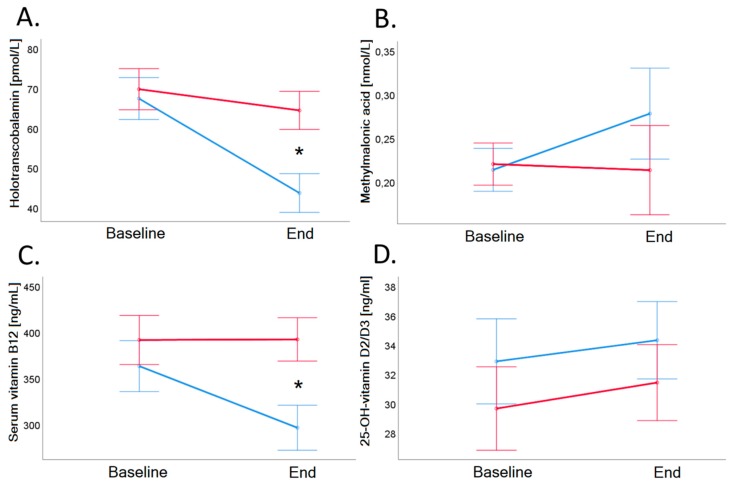
Figure 3.
Holotranscobalamin (Panel A), methylmalonic acid (Panel B), vitamin B12 (Panel C), and 25-OH-Vitamin D2/D3 (Panel D) in serum before and after 4-week dietary intervention in VD (blue line) and MD (red line). Serum vitamin B12 (ng/L) and holotranscobalamin concentrations (pmol/L) showed a significantly decrease in vegans (vitamin B12: 362.8 ± 110.9 to 296.1 ± 94.1 ng/L, p < 0.001; holotranscobalamin: 67.3 ± 23.5 to 43.6 ± 20.0 pmol/L, p < 0.001) compared to meat-rich subjects (vitamin B12: 391.2 ± 159.2 to 391.8 ± 143.0 ng/L, p = 0.919; holotranscobalamin: 69.7 ± 29.7 to 64.4 ± 28.7 pmol/L, p = 0.041). Holotranscobalamin decreased by more than 30% upon dietary intervention, whereas serum vitamin B12 decreased by 18%. Error bars show ± 1 standard error. Baseline and end values as well as statistical comparisons are shown in Table 2. Significant differences between groups are marked with an asterisk (*: p < 0.05).