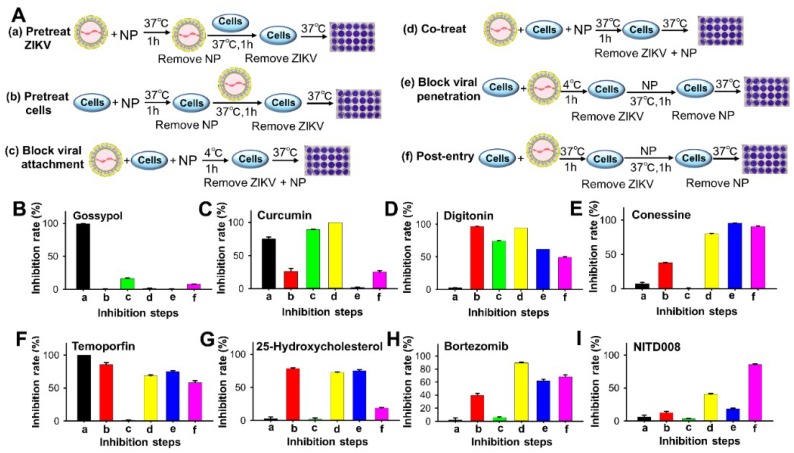
Figure 3.
Time-of-addition experiment to test the ability of natural products to block ZIKV infection at different steps of the viral life cycle [21]. (A) The time-of-addition experiment was performed in Vero E6 cells, and specific procedures are illustrated in detail in (a–f). (a) Pretreatment of ZIKV: ZIKV was incubated with one of the natural products (NPs; including gossypol, curcumin, digitonin, and conessine) at 37 °C for 1 h. After removal of the unbound NPs, the NP-treated ZIKV was incubated with cells at 37 °C for 1 h, followed by culture of the cells at 37 °C for 4–5 days before calculation of plaques. (b) Pretreatment of cells: cells were preincubated with one of the NPs at 37 °C for 1 h, and the unbound NPs were then removed, followed by addition of ZIKV and incubation of cells at 37 °C for 1 h. After removal of the unbound ZIKV, the cells were cultured and plaques were calculated as in (a). (c) Blockage of ZIKV attachment: cells were incubated with ZIKV at 4 °C for 1 h to allow ZIKV attachment, but not fusion between ZIKV and cell membranes, in the presence of one of the NPs. After removal of the unbound ZIKV and NPs, the cells were cultured and plaques were calculated as in (a). (d) Cotreatment of ZIKV and cells: cells were infected with ZIKV at 37 °C for 1 h in the presence of one of the NPs, followed by removal of the unbound viruses and NPs, and culture of the cells to calculate plaques, as in (a). (e) Blockage of ZIKV penetration (membrane fusion): cells were incubated with ZIKV at 4 °C for 1 h to allow ZIKV attachment. After removal of the unbound ZIKV, the cells were incubated with one of the NPs at 37 °C for 1 h to allow fusion of virus–cell membranes. After further removal of the unbound NPs, the cells were cultured and plaques were calculated as in (a). (f) Inhibition of postentry stage: cells were incubated with ZIKV at 37 °C for 1 h to allow ZIKV entry into the target cells. After removal of the unbound ZIKV, the cells were further incubated with one of the NPs at 37 °C for 1 h, followed by removal of the unbound NPs and culture of cells for calculation of plaques, as in (a). Inhibition of natural products, including gossypol (B), curcumin (C), digitonin (D), and conessine (E), against ZIKV (PAN2016) infection in the six steps mentioned above. (F) A potent anti-ZIKV inhibitor, temoporfin [28], was used as a control for step a. (G) An anti-ZIKV entry (especially in inhibition of the internalization/fusion step) inhibitor, 25-hydroxycholesterol [29], was used as a control for steps b and e. Anti-ZIKV compound bortezomib was used as a control for step d (H), and a replication inhibitor, NITD008 [30], for step f (I). The natural product curcumin (C), which has been previously reported to inhibit the attachment of ZIKV to host cells [37], was used as a control for stage c. The percent inhibition was calculated in the presence or absence of serially diluted natural products. The data are expressed as mean ± s.e.m. (n = 2). The experiments were performed in Vero E6 cells and repeated three times, with similar results.