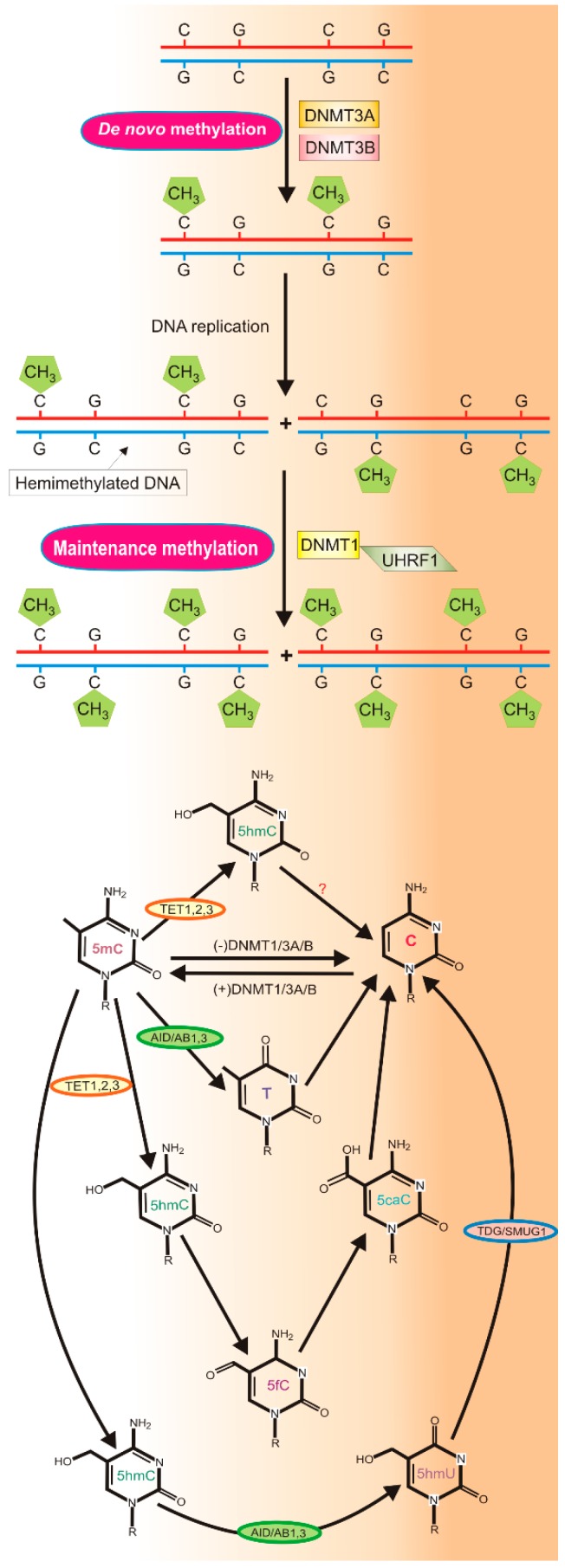
Figure 1.
DNA methylation and demethylation in humans. DNA methylation (upper panel) producing 5-methylcytosine (5mC) is catalyzed by DNA methyltransferases (DNMT). DNMT1 methylates hemimethylated DNA (maintenance methylation) and can be assisted by UHRF1 (ubiquitin like with PHD (plant homeodomain) and ring finger domains 1). DNMT3A and DNMT3B are involved in de novo DNA methylation; 5mC can be reverted to C passively or actively (lower panel) and may undergo spontaneous or activation-induced deaminase (AID)-mediated deamination converting it into thymine (T), which can be replaced with C via DNA repair with TDG (thymine DNA glycosylase) or SMUG1 (single-strand-selective monofunctional uracil-DNA glycosylase 1) glycosylases. Active demethylation is led by the ten eleven translocation (TET) proteins TET1-3 with the following intermediates: 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC), and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC). 5hmC can be converted to 5 hydroxymethyluracil (5hmU) or T.