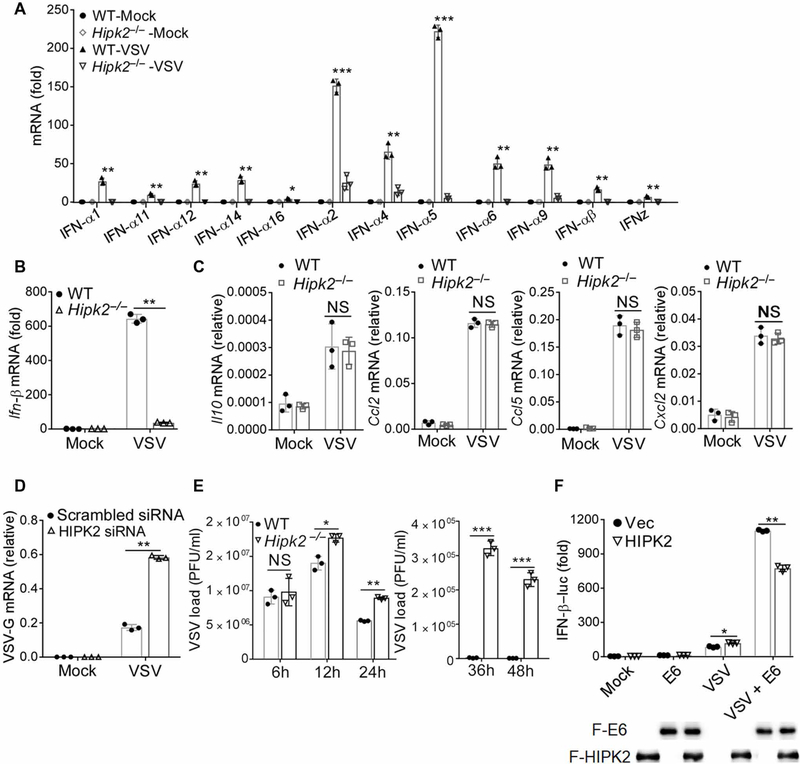
Fig. 3. HIPK2 promotes the expression of type I IFNs.
(A and B) qRT-PCR analysis of Ifnαs (A) and Ifn-β (B) mRNA expression 24 hours after VSV infection of wild-type and Hipk2−/− iBMDMs. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. (C) qRT-PCR analysis of Il10, Ccl2, Ccl5, and Cxcl2 mRNA expression in wild-type or Hipk2−/− iBMDMs after VSV infection for 6 hours. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. (D) qRT-PCR analysis of VSV-G mRNA expression in HEK293 cells transfected with scrambled control or HIPK2 small interfering RNA (siRNA) and infected with VSV for 24 hours. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. (E) Plaque assay analysis of viral production by wild-type or Hipk2−/− iBMDMs infected with VSV for indicated times. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. (F) Luciferase assay analysis of IFN-β promoter activity in HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated expression plasmids and then infected with VSV for 24 hours. Data (top) with means ± SEM are from three experiments. Blots confirming expression of the indicated proteins (lower) are representative of all experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, by Student’s t test