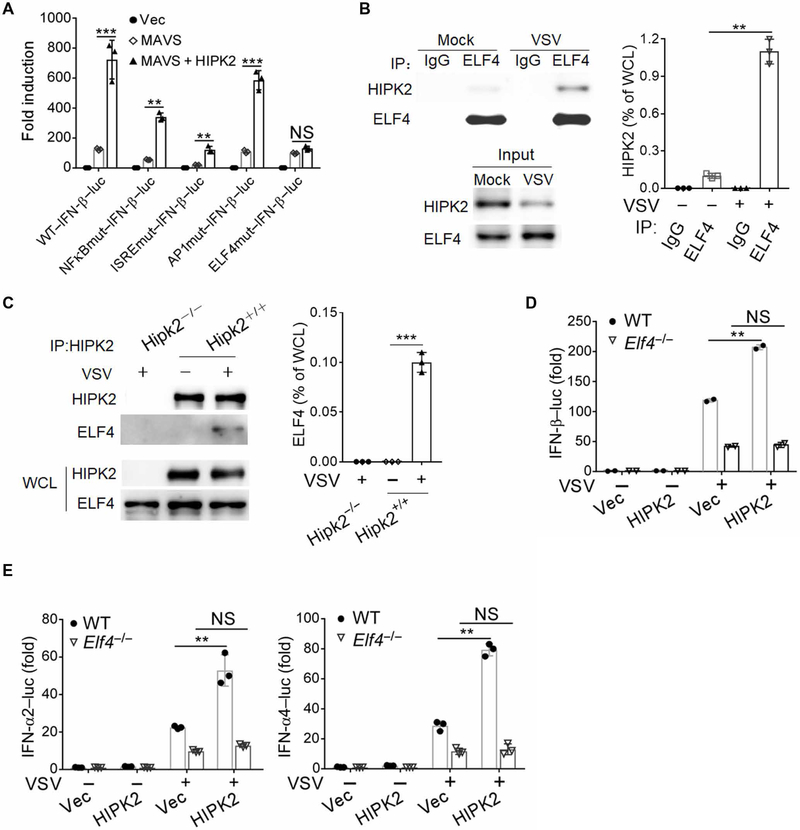
Fig. 5. HIPK2 activates the transcription of IFNs by interacting with ELF4.
(A) Luciferase assay analysis of wild-type and mutant IFN-β promoter activity in HEK293 cells transfected with the indicated expression plasmids for 24 hours. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation analysis of ELF4 interaction with HIPK2 in lysates of HEK293 cells infected with VSV for 6 hours. Blots (left) are representative of three experiments. Quantified HIPK2 band intensity values (right) normalized to whole-cell lysate (WCL) are pooled from all experiments. IP, immunoprecipitation. (C) Coimmunoprecipitation analysis of HIPK2 interaction with ELF4 in lysates of wild-type and Hipk2−/− iBMDMs infected with VSV for 6 hours. Blots (left) are representative of 3 experiments. Quantified HIPK2 band intensity values (right) normalized to WCL are pooled from all experiments. (D and E) Luciferase assay analysis of IFN-β (D) or IFN-α2–luc and IFN-α4–luc (E) promoter activity in wild-type or ELF4−/− HEK293 cells transfected with Vec control or HIPK2 expression plasmids and infected with VSV for 24 hours. Data with means ± SEM are from three experiments. **P < 0.01 and ***P < 0.001 by Student’s t test.