Figure 1.
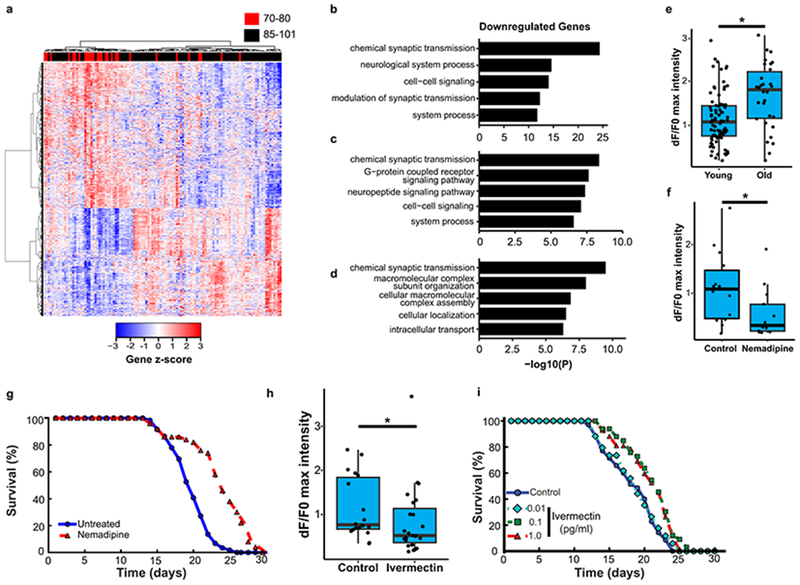
Neural excitation and longevity in humans and C. elegans. a, Analysis of the cortical transcriptome profile in cognitively intact aged individuals from the ROSMAP cohort. Unsupervised hierarchical clustering shows a transcriptional signature of down- and up-regulated genes associated with extended longevity. b-d, Most significantly enriched gene ontology (GO) terms for downregulated genes associated with extended longevity (≥85 versus ≤80 years of age) in the ROSMAP (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, n=117) (b), CommonMind Consortium (dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, n=155) (c), and Gibbs (frontal cortex, n=37) (d) cohorts. P-values were calculated by Fisher’s exact test (see Methods). e, Aging C. elegans exhibit increased neuronal excitation. Shown are the maximum GCaMP fluorescence intensity changes in ASH neurons of young adult (day 1-2) and older (day 12-16) worms. Young, n=82 worms; Old, n=30 worms. *P=3.6e-4 by Mann–Whitney U test. f, The L-type calcium channel blocker nemadipine (2μM) represses neural excitation. Control, n=14; Nemadipine, n=13. *P=0.029, Mann–Whitney U test. g, Nemadipine extends lifespan. Worms were continuously treated with 2 μM nemadipine beginning at adult day 1, P=7.7e-11, log-rank test. Control, n=59; Nemadipine, n=50, replicated 3 times. h, The chloride channel agonist ivermectin (1pg/ml) reduces neural excitation. Control, n=18; Ivermectin, n=23. *P=0.038, Mann–Whitney U test. i, Extension of lifespan by continuous treatment with ivermectin beginning at adult day 1 (Control, n=35; 0.01 pg/ml: n=34, P= 0.62 ; 0.1 pg/ml: n=33, P= 1.5e-3; 1pg/ml: n=42, P= 1.9e-3, log-rank test), replicated 3 times. Summary statistics for all individual lifespan experiments are in Supplementary Table 22.