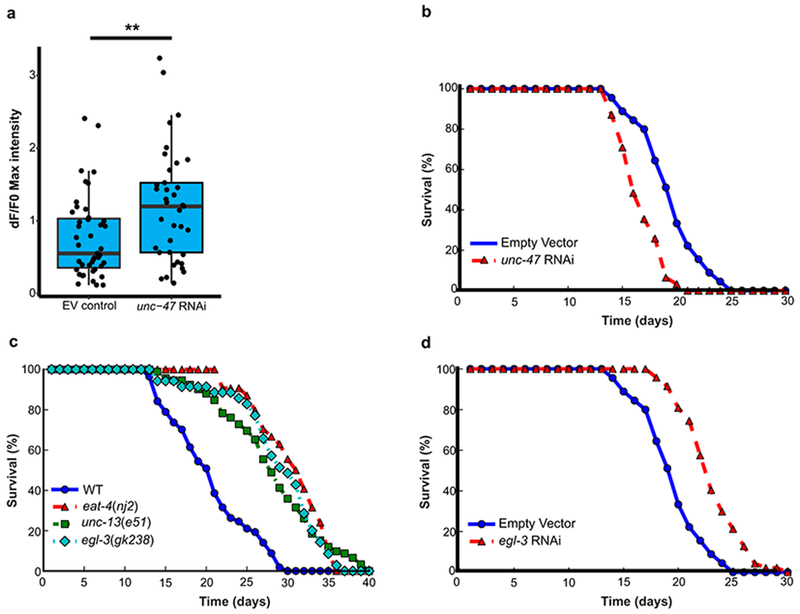
Extended Data Figure 4. Neural excitation, neuropeptide signaling and lifespan in C. elegans.
a, Increased excitation of ASH neurons following RNAi against the GABA vesicular transporter unc-47. GCaMP imaging was performed on worms with enhanced neuronal RNAi (See Figure 3 legend and Methods for details) for unc-47 (n=37) or controls (n=43) at day 2. **P= 6.8e-3 by the Mann–Whitney U test. b, RNAi for unc-47 reduces lifespan. Worms with enhanced neuronal RNAi were treated with unc-47 (n=31) or control RNAi (n=84). Shown is a representative lifespan analysis replicated 3 times. P= 1.3e-6 by log-rank test. c, Reduction of synaptic neurotransmission or neuropeptide signaling extend lifespan in C. elegans. Mutations in genes affecting glutamatergic neurotransmission (eat-4), presynaptic function (unc-13) and neuropeptide signaling (egl-3) exhibit comparable lifespan extension. WT, n=57; eat-4(nj2), n=54. P≤2.2e-16; unc-13(e51), n=92, P=3.6e-14; egl-3(gk238), n=35, P=8.3e-11 by log-rank test. Shown are curves representative of two independent replicates. d, Extension of lifespan by egl-3 RNAi in worms with enhanced neuronal RNAi. Shown are lifespan curves representative of two independent replicates. egl-3 RNAi (n=47 worms); Empty Vector (n=84 worms). P=3.5e-11 by the log-rank test.