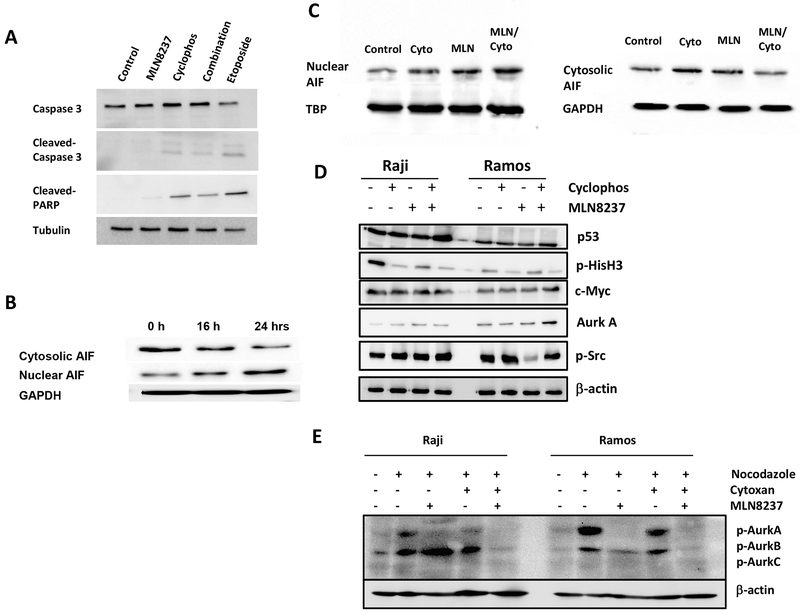
Figure 5.
AURKA inhibition induces caspase-independent apoptosis. (a) Induction of caspase-3 and PARP cleavage by immunoblotting in Raji cells treated with PBS (negative control), cyclophosphamide, MLN8237, combination of cyclophosphamide and MLN8237, or etoposide (positive control) at 24 hours. (b) Nuclear and cytosolic AIF in Raji cells treated with PBS control, cyclophosphamide, MLN8237, or combination of cyclophosphamide and MLN8237. (c) Cytosolic and nuclear AIF levels over time in Raji cells treated with MLN8237 at 8, 16, and 24 hours. (d) c-Myc, total AURKA, Src, and p53 protein levels in Raji cells treated with PBS control, cyclophosphamide, or MLN8237 at 24 hours. (e) p-AURK A, B, and C levels in Raji cells treated with PBS control, nocodazole (p-AURK inducer), cyclophosphamide, and/or MLN8237 at 24 hours.