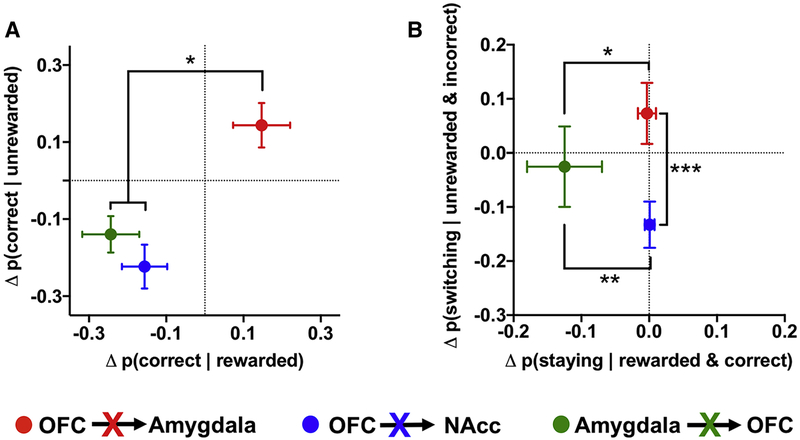
Figure 8:
Behavioral dissociation of OFC circuit contributions to reinforcement learning. (A) The change in the probability of making a correct choice following a rewarded trial (x axis) plotted against the change in the probability of making a correct choice following an unrewarded trial (y axis) following ablation of the OFC→NAcc (blue), OFC→Amygdala (red) or Amygdala→OFC (green) circuit. (B) The change in the probability of staying with a rewarded and correct choice (x axis) plotted against the change in the probability of switching from an unrewarded and incorrect choice (y axis) following ablation of the OFC→NAcc, OFC→Amygdala or Amygdala→OFC circuit. Difference scores were calculated by subtracting the post-DT probabilities from the pre-DT probabilities and compared using Mann-Whitney tests. * p<0.05; ** p<0.01; *** p<0.001.