Figure 2. Frequency and effect size of neuroblastoma-associated mutations.
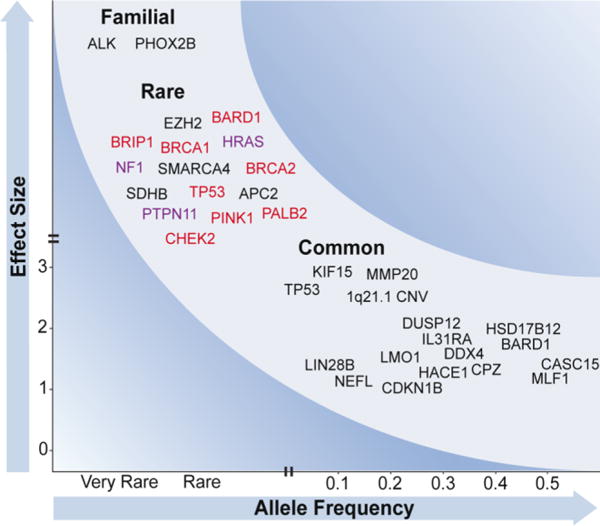
Variants contributing to neuroblastoma risk range from rare variants of large effect to common variants of small effect. (Top left) Familial mutations in ALK and PHOX2B have been identified through linkage-based studies and evaluation of cases with associated conditions. Other rare damaging variants in cancer-associated genes have been observed in sporadic neuroblastoma by sequencing, but their true frequency and impact is unknown. Several mutations affect genes involved in DNA repair (red) and Ras-MAPK signaling (purple). (Bottom right) Common polymorphisms identified through GWAS predispose to sporadic neuroblastoma, likely through cooperative effects. These variants are plotted at the observed minor allele frequencies and odds ratios.
