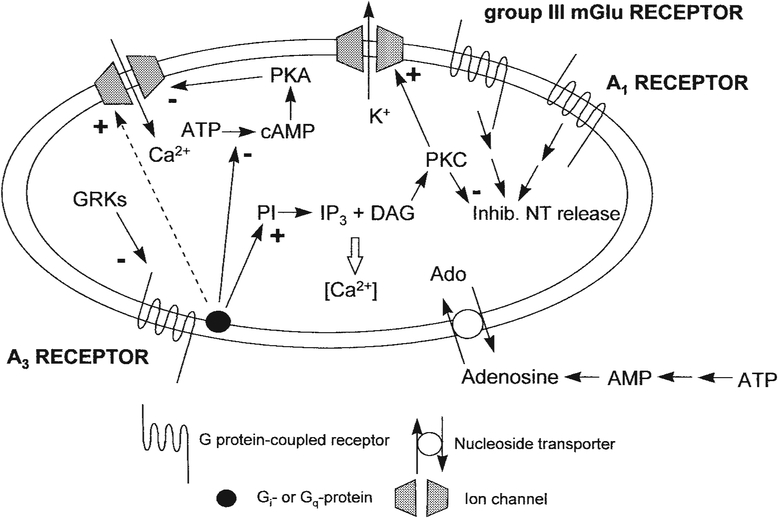
Fig. 1.
Processes resulting from activation of A3 adenosine receptors. The dashed line indicates activity only at micromolar concentrations of IB-MECA [Kohno et al., 1996; Casavola et al., 1998]. Presynaptic hippocampal A3 receptor activation induces inhibition of the effects of A1 receptors [Dunwiddie et al., 1997] and a PKC-dependent inhibition of mGlu receptors [Macek et al., 1998]. In CA3 pyramidal neurons, potentiated calcium current through a protein kinase A (PKA)-dependent mechanism [Fleming and Mogul, 1997]. In cardiac myocytes, A3 receptor activation is proposed to induce PKC-dependent activation of ATP-sensitive K+ channels, which results in cardioprotection [Stambaugh et al., 1997]. PI, phosphatidyl inositol; PKC, protein kinase C; DAG, diacylglycerol; NT, neurotransmitter; GRKs, G-protein-coupled receptor kinases.