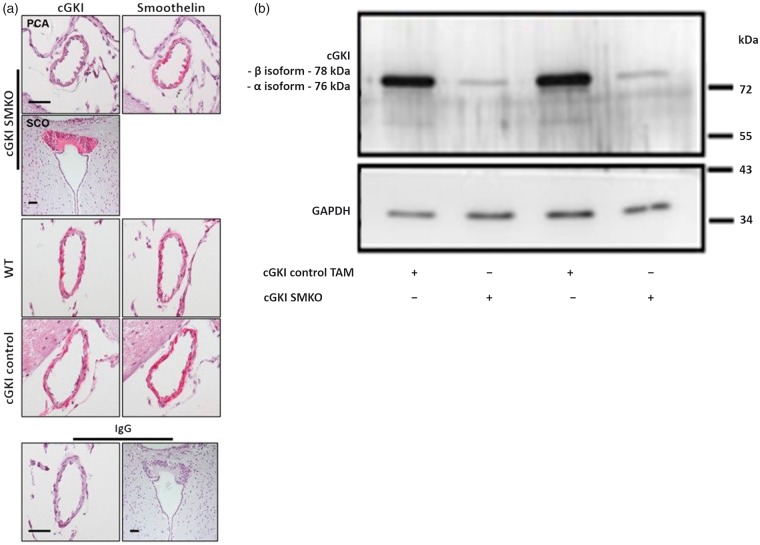
Figure 1.
(a) Cerebrovascular expression of cGKI in cGKI SMKO and control mice. Posterior communicating arteries exhibit cGKI immunoreactivity in cGKI control and WT mouse in vascular smooth muscle cells (left panels, red color), which are identified by their location within the vessel wall and their reaction with an anti smoothelin antibody in subsequent brain sections (right panels, red color). However, cGKI expression was not detected in smooth muscle cells of cGKI SMKO mice; the anti-cGKI antibody reactivity in smooth muscle cells of these vessels is similar to that detected in cells in sections exposed to non-immune IgG (lower panel). Immunostaining of the SCO shows cGKI immunoreactivity in cGKI SMKO mice, demonstrating the smooth muscle cell-specificity of the cGKI knockout in the mice. Counterstaining was performed with hematoxylin. Original magnification, × 60; the bar is 40 µm-long. (b) Ablation of cGKI in aorta of cGKI SMKO mice. Representative Western blot demonstrating control levels of cGKI in aortae of cGKI control TAM mice and lower levels of cGKI in cGKI SMKO mice.