Figure 3.
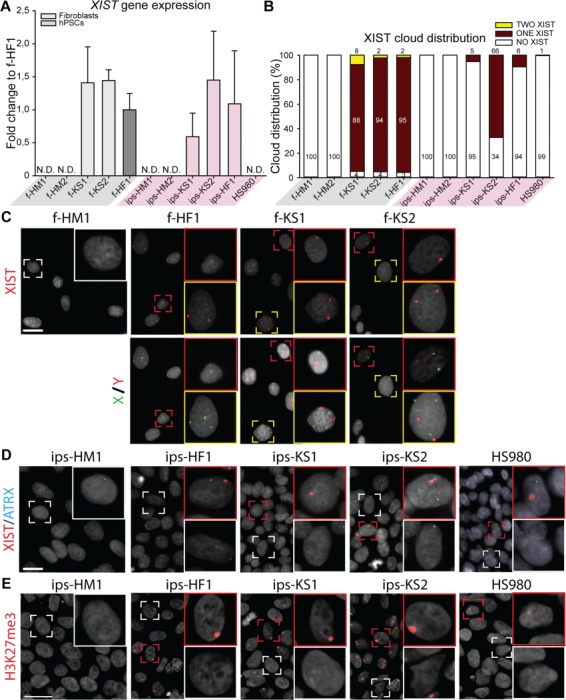
X chromosome inactivation (XCI) analysis of KS fibroblasts and hiPSCs indicates different XCI states. (A) Gene expression level of XCI marker, XIST, relative to female fibroblasts (f-HF1). Mean expression of three biological replicates with ±SD; N.D. means no detection. (B) Distribution of XIST cloud expression in each cell line based on RNA FISH: one cloud (red), no cloud (white), or two clouds (yellow). Total count from three independent experiments, with >193 cells counted per cell line. (C) Upper panel shows representative images of RNA fluorescence in situ hybridization (FISH) with one (red square) or two (yellow square) XIST clouds in HF (f-HF1) and KS (f-KS1 and f-KS2) fibroblasts. HM fibroblasts (f-HD1) were used as negative control showing no clouds (white square). Lower panel shows DNA FISH for X chromosome (green) and Y chromosome (red) for upper panel cells. DAPI (gray) was used as counterstaining. Scale bar is equal to 50 μm. (D) Representative images of RNA FISH with one (red square) or no (white square) XIST (red) cloud in HF (ips-HF1 and HS980) and KS (ips-KS1 and ips-KS2) hPSCs. HM hiPSCs (ips-HM1) were used as negative control showing no XIST (red) clouds. Active transcription site of ATRX is shown in blue. DAPI (gray) was used as counterstaining. Scale bar is equal to 50 μm. (E) Immunostaining of hPSCs for silencing methylation mark, H3K27me3 (red), with positive accumulation mark (red square) or no staining (white square). DAPI (gray) was used as counterstaining. Scale bar is equal to 50 μm.
