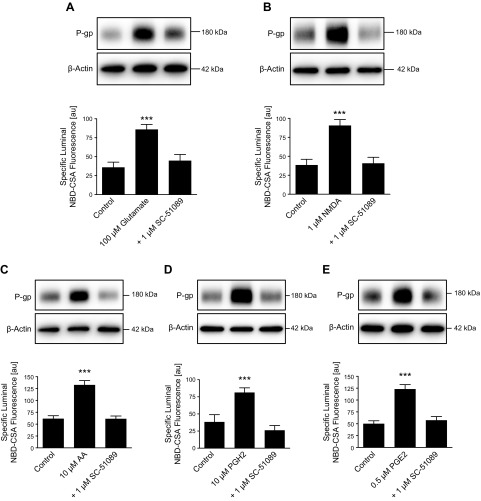
Figure 3.
Glutamate increases P-gp protein and activity levels by signaling through the prostaglandin E receptor EP1. Isolated rat brain capillaries were exposed to glutamate (A), NMDA (B), AA (C), prostaglandin H2 (PGH2) (D), and PGE2 (E) with or without the EP1 inhibitor SC-51089. Blocking the EP1 receptor with SC-51089 fully abolished the action of glutamate, NMDA, AA, PGH2, and PGE2. P-gp protein expression was assessed by Western blotting; β-actin was used as protein loading control. P-gp transport activity was measured as specific luminal NBD-CSA accumulation in capillary lumens. For specific luminal NBD-CSA fluorescence, data represent means ± sem for 10 capillaries from a single preparation (pooled tissue from 10 rats). Units are arbitrary units (au; scale: 0–255). ***P < 0.001, significantly higher than controls.