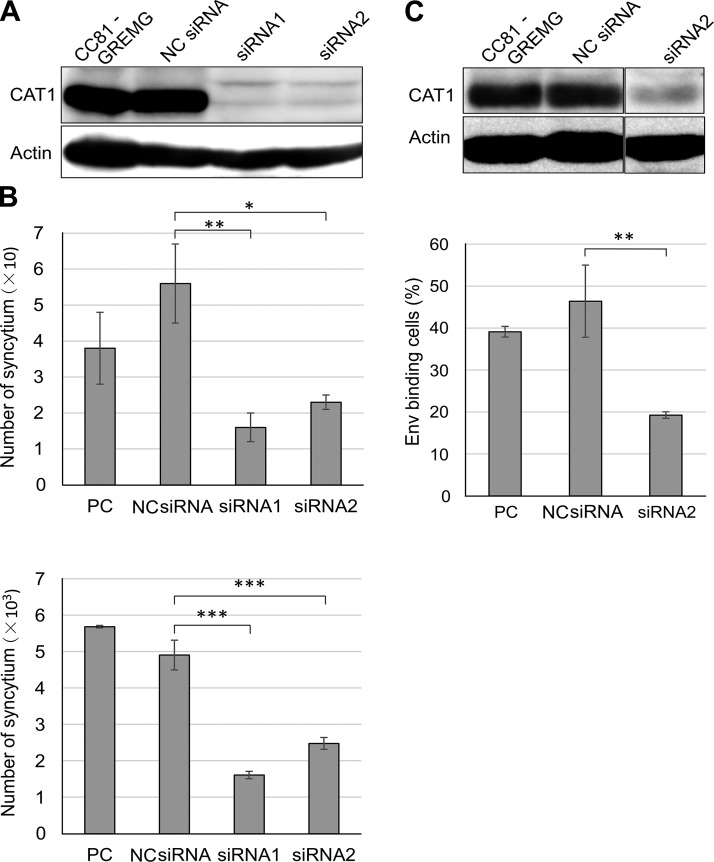
Figure 5.
CAT1/SLC7A1 knockdown reduced BLV infection. A) CAT1/SLC7AI knockdown in CC81-GREMG cells. CC81-GREMG cells were transfected with 2 CAT1-specific siRNAs targeting different regions of CAT1/SLC7A1 or with nonspecific siRNA as a negative control (NC). The cell extracts were prepared at 48 h post-transfection and then subjected to Western blot analysis using anti-CAT1 (upper panel) and anti–β-actin antibodies (lower panel). B) CAT1/SLC7A1 knockdown suppressed cell-free and cell-to-cell BLV infection. The siRNA-transfected CC81-GREMG cells were washed and then cocultured either with culture supernatant of FLK-BLV cells (upper) or FLK-BLV cells (lower) for 48 h and EGFP-expressing syncytia were detected using EVOS2 fluorescence microscopy. Each column and error bar represents the mean + sd of results from triplicate experiments. C) Env binding decreased in CAT1/SLC7A1 knockdown CC81-GREMG cells. CC81-GREMG cells were transfected with siRNA for 48 h. The transfected cells were harvested, and CAT1 expression levels were analyzed by Western blot using an anti-CAT1 antibody. Actin was used as a loading control. CAT1 knockdown CC81-GREMG cells were added to BLV particles enriched from the culture supernatant of FLK-BLV cells and allowed to bind for 2 h at 4°C. BLV Env binding cells were detected using anti-gp51 mAb (BLV-1) followed by incubation with APC-conjugated anti-mouse IgG. After staining, the cells were analyzed using a BD Accuri C6 Plus flow cytometer (lower panel). Each column and error bar represents the mean + sd of results from triplicate experiments. *P = 0.05, **P = 0.01, ***P = 0.001 (Student’s t test).