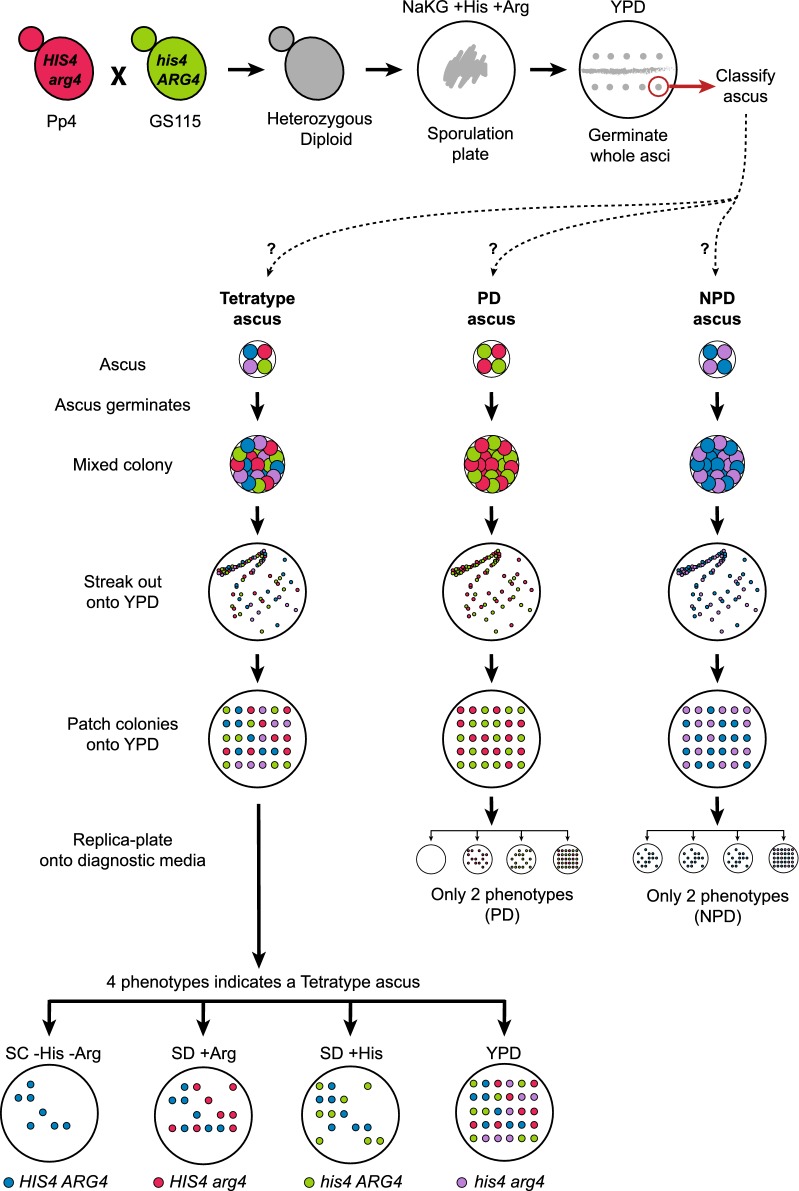
Fig. 3.
Experimental approach used to recover the four products of meiosis from an ascus without tetrad dissection. Parental strains Pp4 and GS115 were crossed to generate the resultant prototrophic heterozygous diploid. This diploid strain was sporulated under nitrogen-limiting conditions (NaKG + His + Arg medium). Whole asci containing four spores were picked up using a dissection microscope and placed on a YPD plate to germinate. The lower part of the diagram summarizes how asci were subsequently classified as tetratype, PD (parental ditype), or NPD (non-parental ditype) after streaking out and replica-plating. After germination, an ascus produces a mixed colony that contains a mixture of either 4 types of haploid cell (if the ascus is tetratype), or 2 types of haploid cell (if the ascus is PD or NPD), with respect to the HIS4 and ARG4 markers. After streaking out this mixed colony onto a fresh YPD plate and incubating for 2 days, single cells give rise to new colonies that each have a homogeneous genotype. These colonies are then patched in a grid pattern on another YPD plate, which is then replica-plated onto diagnostic media that allow the genotype of each colony to be inferred, hence enabling us to infer whether the ascus was tetratype, PD, or NPD. For asci inferred to be tetratype, the 4 types of haploid colonies (segregants) were retained for genome sequencing. For asci inferred to be PD or NPD, the segregants were discarded because it is not possible to identify all 4 products of the meiosis from their colony phenotypes. SC − His − Arg is synthetic complete media made without histidine and arginine. SD + Arg and SD + His are synthetic defined media supplemented with arginine or histidine. YPD is yeast peptone dextrose media (contains all amino acids)