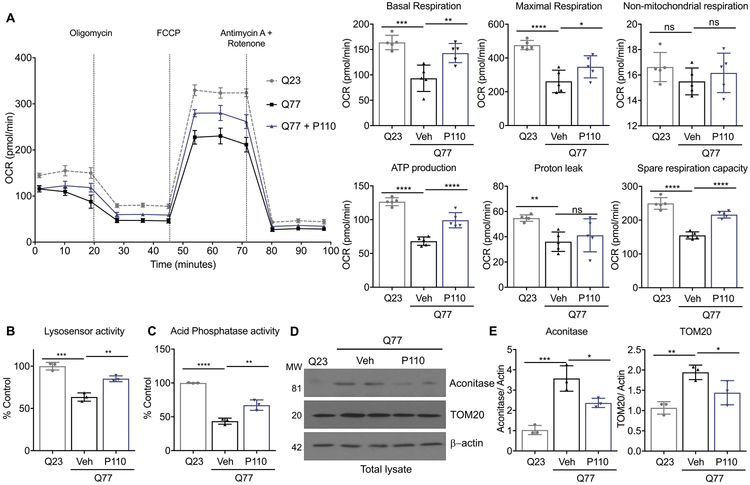
Figure 4. Expanded poly-Q (Q77) expression in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes leads to bioenergetic failure and lysosomal dysfunction.
A. Metabolic health in human iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes stably expressing Q23 (control) or Q77 (as a HD model) 48 hours treated with P110 (1μM once24 h) or Veh, in serum free- galactose medium was measured with Seahorse extracellular flux analyzer. B. Lysosomal function was measured using LysoSensor™ Yellow/Blue DND-160 in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, treated as in A. C. Acid phosphatase activity as a secondary readout for lysosomal function was measured in iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes, treated as in A.D. Levels of aconitase (E) and TOM20 (F) were determined by immunoblotting in total lysates, quantified and presented as ratio vs actin, loading control, from cells treated as in A. Data were evaluated by one-way ANOVA and Holm-Sidak's multiple comparisons test for multiple testing between each treatment group. **** p-value <0.0001; *** p-value <0.001; ** p-value <0.01; * p-value <0.05. All graphs represent mean ± s.d. n=3-5, as indicated in each panel.