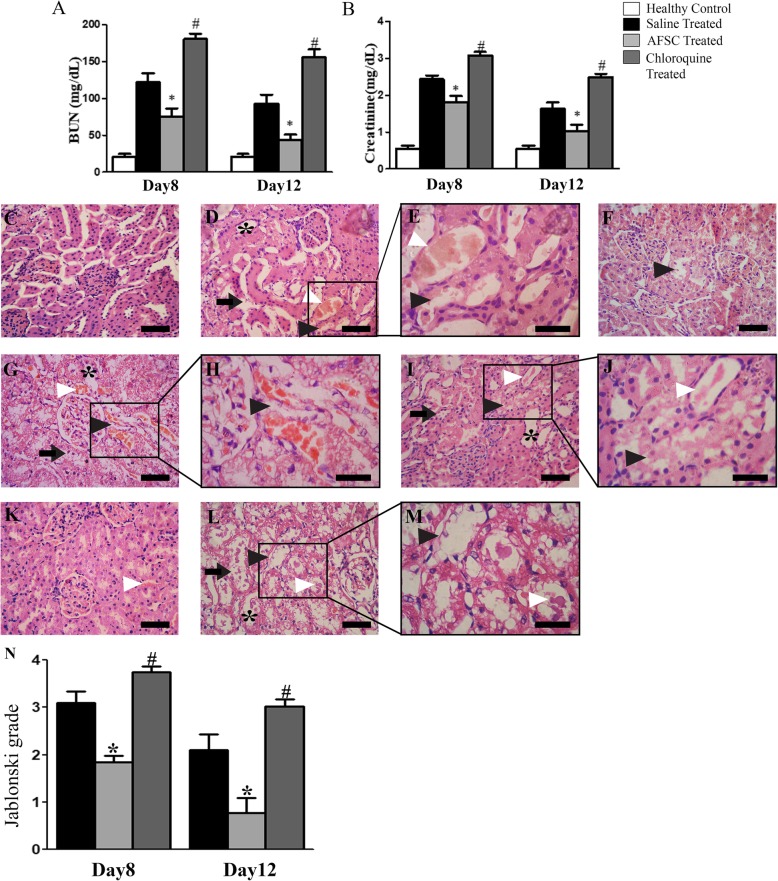
Fig. 7.
Effect of chloroquine administration on renal function and histology in rats with cisplatin-induced ARF. a Levels of blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and b serum creatinine measured in healthy controls, saline-treated, AFSC-treated, and chloroquine-treated ARF rats on days 8 and 12 following cisplatin injection. Values expressed as mean ± SE (*p < 0.05 versus saline-treated group; #p < 0.001 versus therapy-treated group). Representative photomicrographs showing histology of cortical kidney tissue sections from healthy control (c), day 8 saline-treated ARF group (d) showing necrotic tubules (black arrowhead) and intratubular hyaline casts (white arrowhead) in higher magnification (e), day 8 AFSC treated ARF group (f), day 8 chloroquine-treated ARF group (g) showing necrotic tubules (black arrowhead) in higher magnification (h), day 12 saline-treated ARF group (i) showing necrotic tubules (black arrowhead) and intratubular hyaline casts (white arrowhead) in higher magnification (j), day 12 AFSC-treated ARF group (k), and day 12 chloroquine-treated ARF group (l) showing necrotic tubules (black arrowhead) and intratubular hyaline casts (white arrowhead) in higher magnification (m). The kidney sections of day 8 and day 12 chloroquine-treated ARF rats show severe tubular necrosis (black arrowhead) with intratubular hyaline casts (white arrowhead), tubular dilatation (asterisk), and loss of brush border (black arrow) as compared to other groups. n Jablonski grading score for the assessment of tubular necrosis in saline-treated, AFSC-treated, and chloroquine-treated groups on day 8 and day 12 after cisplatin injection. Values expressed as mean ± SE (*p < 0.05 versus saline-treated group; #p < 0.001 versus AFSC-treated group)